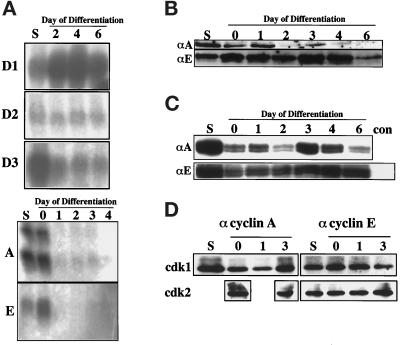
Figure 4.
Expression of G1- and S- phase cyclins in differentiating Rcho-1 cells. (A) Analysis of mRNAs for the D-type cyclins, cyclin A2, and cyclin E. Total RNA was isolated from proliferating (S) and differentiating Rcho-1 cells at various times after removal of the proliferating cells by trypsinization. Each sample contains 10 μg of total mRNA separated and hybridized to the cyclin probe indicated on the left of each panel. (B) Immunoblot analysis of cyclin A and E proteins in differentiating Rcho-1 cells. The samples were normalized for amount of protein. The proteins were separated on a 10% polyacrylamide gel, transferred, and the proteins were detected by using the primary antibody indicated in the panels (αA = α-cyclin A antibody; αE = α-cyclin E antibody). (C) Determination of kinase activity associated with the cyclins A and E. The lysates used for the immunoblot analysis were subjected to immunoprecipitation using the anti-cyclin antibodies. The immunoprecipitates were assayed for cyclin-associated histone-kinase activity and analyzed by separating the products on a 12.5% polyacrylamide gel. Autoradiographs of the phosphorylated histone H1 are shown with the immunoprecipitating antibody indicated on the left of each panel. A negative control, performed by omitting the primary antibody and using the stem-cell lysate in a mock immunoprecipitation–kinase reaction, is included as the right-most lane shown in the panel with the cyclin E-immunokinase assays. (D) Coimmunoprecipitation of p34cdk1 and p33cdk2 with cyclin A and E. The immunoprecipitates collected with the anti-cyclin A or E antibodies were subjected to gel electrophoresis and were immunoblotted using anti-p34cdk1 or anti-p33cdk2 antibodies. The lysates used for the immunoprecipitates are the same as those used for the histone H1 kinase assays; however, only lysates from the proliferating cells and differentiating cells at d 0, 1, and 3 were analyzed, as these contain the greatest amounts of cyclin-associated kinase activity.