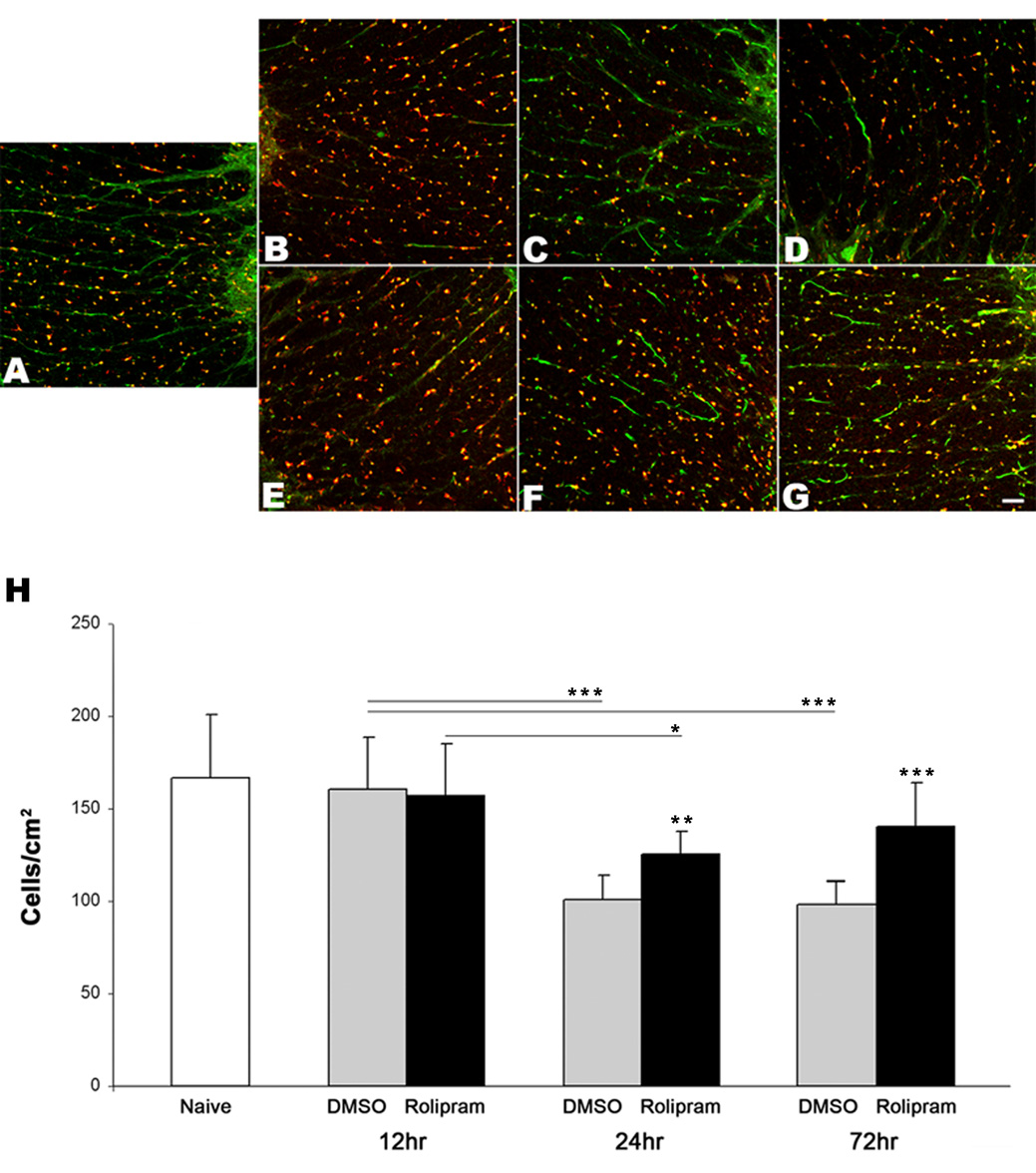
Figure 2.
Oligodendrocytes are spared after SCI by rolipram treatment. Representative transverse sections show APC (red)-and PKA (green)-immunopositive oligodendrocytes in the C5–C6 spinal cord VLF of a normal rat (A) and of both DMSO-treated rats (B–D), and rolipram-treated rats (E–G) 12 (B, E), 24 (C, F), and 72 (D, G) hours post-contusive cervical SCI. Comparisons between the numbers of APC- and pPKA-immunopositive oligodendrocyte somata in the C5–C6 spinal cord VLF of normal rats (n=4) and injured rats (n=4 for each group at each time point except that n=3 for rolipram-treated rats at 72 hours) revealed a significant reduction in both treated groups at 24 and 72, but not at 12, hours post-SCI (H). In contrast to DMSO, rolipram treatment significantly attenuated this loss. Significantly more oligodendrocyte somata continued to be seen in rolipramtreated rats’ VLF at 72 hours post SCI compared to DMSO-treated rats. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. Error bars represent standard deviations. Scale bar=50µm.