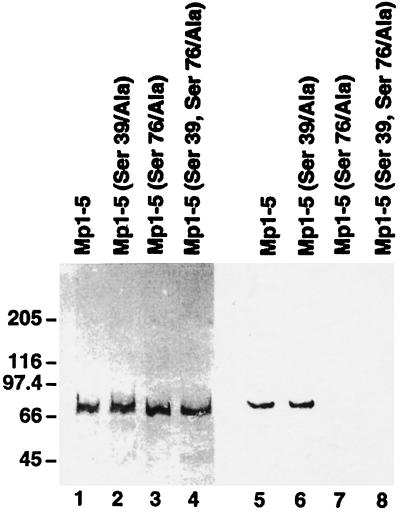
Figure 5.
In vitro phosphorylation of mutant recombinant M-protein fragments. Purified EEF-tagged Mp1–Mp5 fragments were phosphorylated in vitro by PKA and 32P-labeled ATP and run on two identical 4–10% gradient polyacrylamide gels. One gel was blotted to nitrocellulose and stained with the antibody recognizing the EEF-tag and a peroxidase-coupled secondary antibody (lanes 1–4), while the second gel was dried and autoradiographed (lanes 5–8). Lanes 1–4 contain approximately identical amounts of Mp1–Mp5 (lane 1), Mp1–Mp5 (Ser39/Ala) (lane 2), Mp1–Mp5 (Ser76/Ala) (lane 3), and Mp1–Mp5 (Ser39, 76/Ala) (lane 4). Lanes 5–8 show that Mp1–Mp5 and its (Ser39/Ala) mutant are phosphorylated, while phosphorylation of both mutants containing the Ser76/Ala mutation (lanes 7 and 8) is almost completely abolished. Thus Ser76 is the PKA phosphorylation site of M-protein.