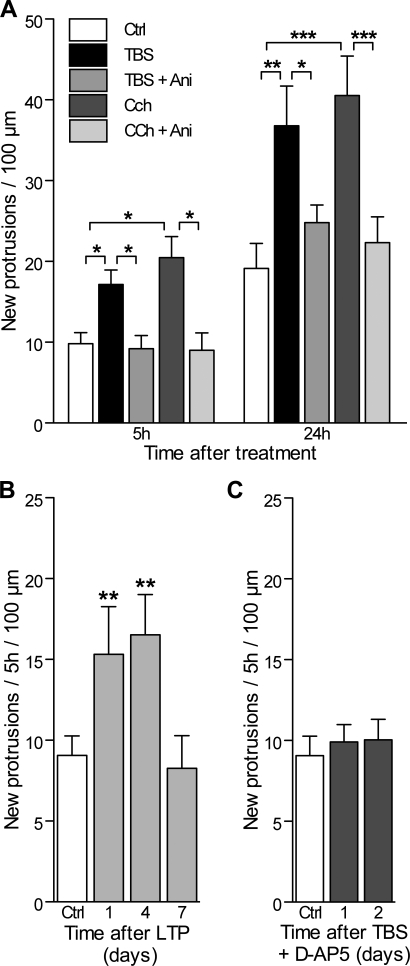
Figure 3. Increased Activity-Induced Protrusion Formation Is Protein Synthesis Dependent and D-AP5 Sensitive.
(A) Number of new protrusions (spines and filopodia) per 100 μm of dendritic length detected during the first 5 h and 24 h in control slice cultures (open columns), following TBS stimulation (black columns) or TBS applied in the presence of the protein synthesis inhibitor Ani (25 μM; grey columns; n = 6 cells/351 protrusions), as well as following Cch treatment (dark grey columns) and Cch together with Ani (light grey columns; n = 6 cells/307 protrusions). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-tests.
(B) The number of new protrusions formed per 5 h and per 100 μm of dendritic length was measured under control conditions (n = 15 cells), and at 1, 4, and 7 d after LTP induction (n = 8). **p < 0.01, one-way ANOVA with Dunnett post-tests.
(C) Rate of protrusion formation measured 1 and 2 d after TBS applied in the presence of 100 μM D-AP5 (n = 7).