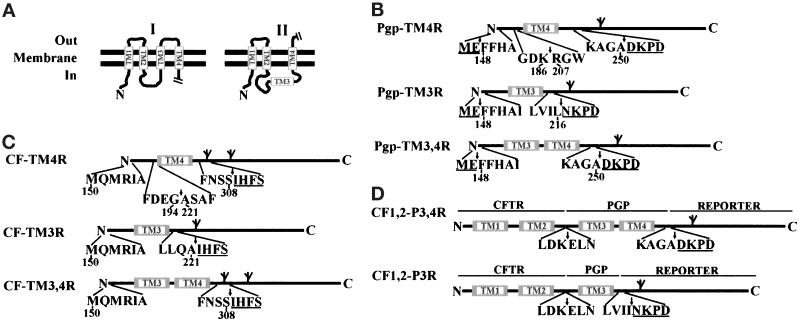
Figure 1.
(A) Topological models of a partial sequence of Pgp. Model I is the predicted topology with all TM segments in the membrane. Model II is the alternative topology with TM3 in cytoplasm and TM4 in an Nin-Cout orientation. (B, C, and D) Diagram of constructs used to characterize TM3 and TM4 of Pgp (B and D) and CFTR (C). Each fusion site is indicated by an arrow. The potential glycosylation sites are shown as branched symbols. The underlined amino acids (in single-letter code) are residues from the reporter peptide. Note that the reporter peptide in CF-TM4R and CF-TM3,4R has two potential N-linked glycosylation sites (Chen and Zhang, 1996).