Figure 3. MRI studies of the effects of endothelial myrAkt1 on blood volume and vascular permeability.
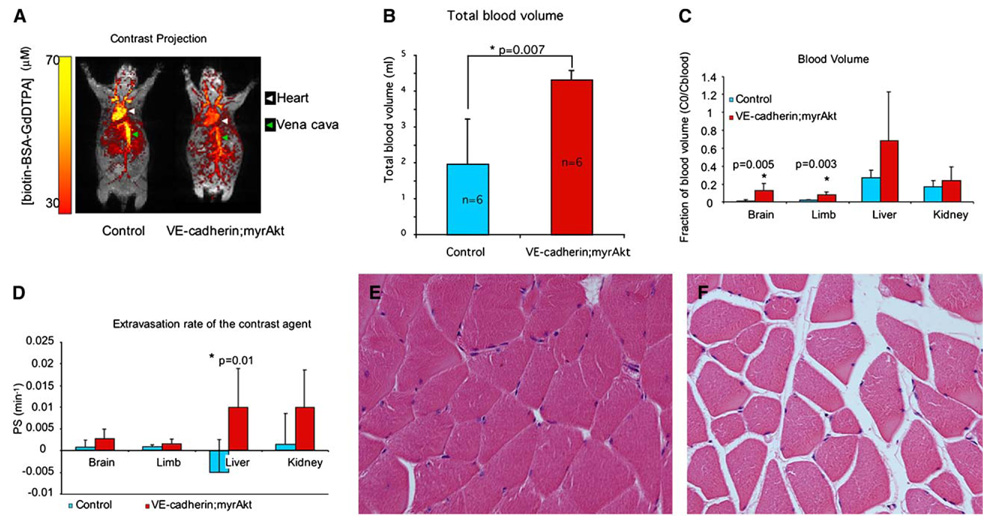
A: Mice were taken off tetracycline for 7 days, then imaged by dynamic contrast enhanced MRI using intravenously administered biotin-BSA-Gd-DTPA. The intravascular distribution of contrast agent in vivo is seen in overlay of maximal intensity projections maps from images that were taken prior to contrast injection (gray) and immediately after contrast injection (color).
B: Total blood volume was significantly higher in myrAkt1 double transgenic mice than in control mice (p = 0.007; n = 6 mice per group).
C: Significant changes in blood volume fraction (fBV) were observed in the brain and hindlimb of double transgenicmice as compared to control mice (brain, p = 0.005; hindlimb, p = 0.003; n = 6 mice per group).
D: Increased permeability surface area product (PS) was observed in the brain, limb, liver, and kidney, with statistically significant differences seen in the liver (p = 0.01; n = 6 mice per group).
E and F: Edema is seen in skeletal muscles in double transgenic mice as shown by separation of muscle fibers in these mice (F) as compared to controlmice (E). Bars in graphs represent means ± standard deviations.
