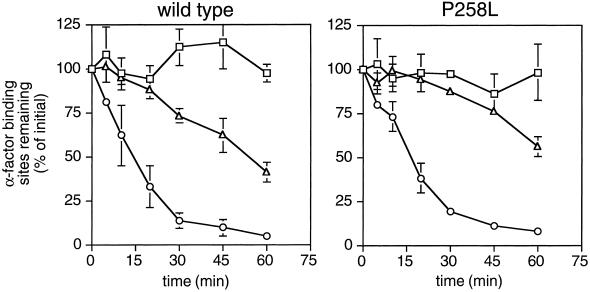
Figure 2.
Internalization of wild-type and constitutively active α-factor receptors. The wild-type STE2 or ste2P258L alleles were expressed from their normal promoters on centromere-containing plasmids (pRS314 derivatives) in a ste2Δ mutant (KBY16). Assays of basal and agonist-induced internalization of wild-type receptors (left panel) and constitutively active α-factor receptors (expressed from the ste2P258L allele; right panel) were performed by determining the number of cell surface α-factor–binding sites remaining as a function of time. Rates of receptor internalization were determined in the absence of α-factor (triangles) and in response to unlabeled α-factor (circles) that was stripped from cells before radioligand binding assays were performed. As a control, the stability of cell surface receptors (squares) was determined by inhibiting internalization (with NaN3 and KF) and determining the number of ligand-binding sites remaining over time. Data shown are the average of duplicate assays of two independent transformants expressing wild-type or constitutively active receptors; standard deviations are indicated.