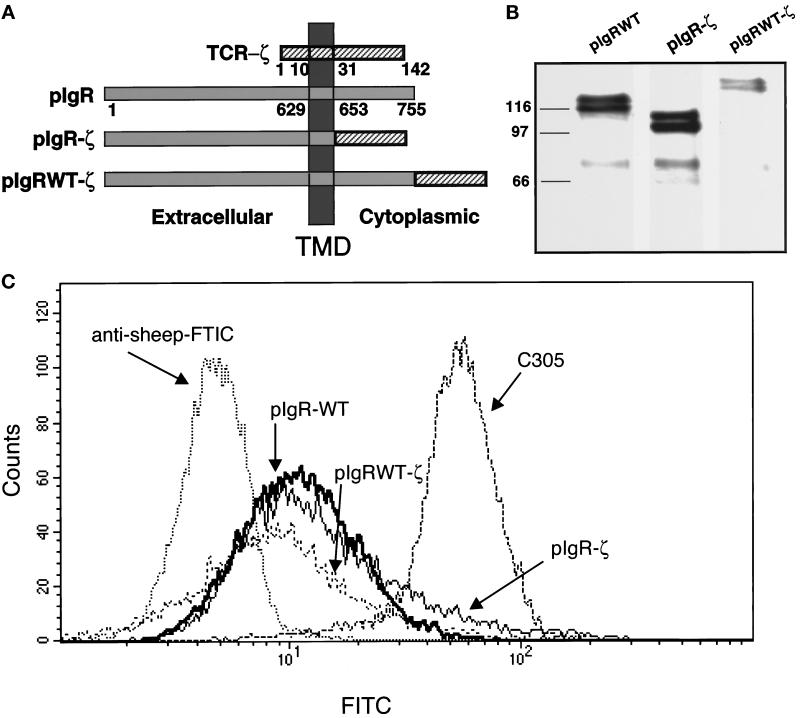
Figure 1.
Construction and stable expression of pIgR-ζ chimeras in Jurkat cells. (a) A schematic representation of the pIgR-WT, pIgR-ζ, and pIgRWT-ζ constructs. The extracellular, TMD, and cytoplasmic tails are indicated. Numbers correspond to amino acids after signal peptide cleavage. (b) Stable expression of pIgR-WT, pIgR-ζ, and pIgRWT-ζ in Jurkat cells selected with G418 (2 mg/ml). Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated for pIgR with guinea pig anti-SC conjugated to Protein A-Sepharose, separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and transferred to immobilon P for detection by Western blot. The pIgR constructs were detected with sheep anti-SC, followed by HRP-labeled secondary antibody. The molecular weight markers in kilodaltons are indicated on the right. Note that each construct migrates as a dimer, due to heterogeneous glycosylation, as previously observed. The bands around 70 kDa are SC, which is cleaved from the pIgR due to the extremely protease-sensitive site where this cleavage normally occurs. (c) Flow cytometry was used to analyze cell surface expression of pIgR-WT, pIgR-ζ, and pIgRWT-ζ. Jurkat cells (1–2 × 106) were cooled to 4°C and stained with sheep anti-SC antibody followed by anti-sheep FITC-conjugated secondary antibody.