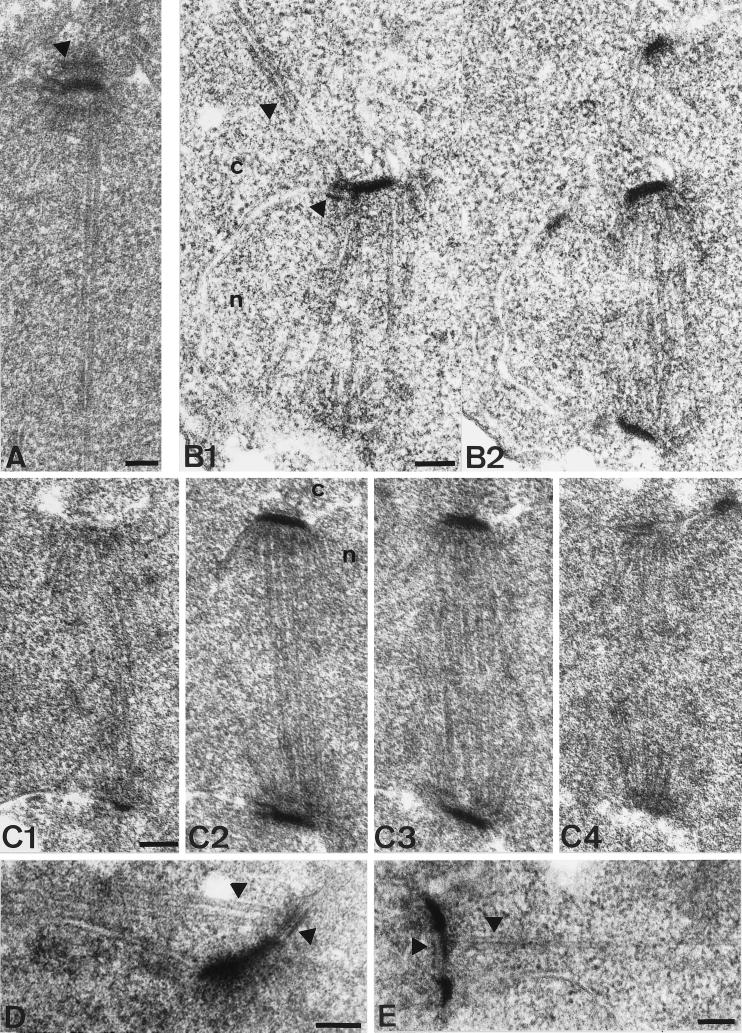
Figure 4.
Thin section electron microscopy of wild-type and cnm67Δ1 spindles. The nucleus is marked by ’n’ and the cytoplasm by ’c’. (A) SPB of a wild-type cell with elongated spindle. The SPB half-bridge as well as the central, inner, and outer plaque of the SPB are visible. The arrowhead shows the outer plaque. Cytoplasmic microtubules do not lie within the plane of the section. (B1–2) Serial thin sections of a complete cnm67Δ1 spindle after SPB separation. Unlike in wild-type cells, cytoplasmic microtubules are attached to the half-bridge of the upper SPB. Arrowheads show cytoplasmic microtubules and the half-bridge. (C1–2) Serial thin sections of a cnm67Δ1 spindle. The SPB outer plaque is not detectable in any of the sections, although the half-bridge, central, and inner plaques appear normal. The same was found for all cnm67Δ1 SPBs that we investigated (n>300). (D) Cytoplasmic microtubules are attached to the half-bridge of a cnm67Δ1 cell with a single SPB, presumably a G1 cell. Arrowheads show the half-bridge and cytoplasmic microtubules. (E) Side- by-side SPBs are connected by a bridge that nucleates cytoplasmic microtubules directing into the bud. The bridge and cytoplasmic microtubules are indicated. Bars, 0.1 μm.