Fig. 2. Sites Within the Catalytic Domain but not the Heavy Chain Mediate the Binding of FXIa to Activated Platelets.
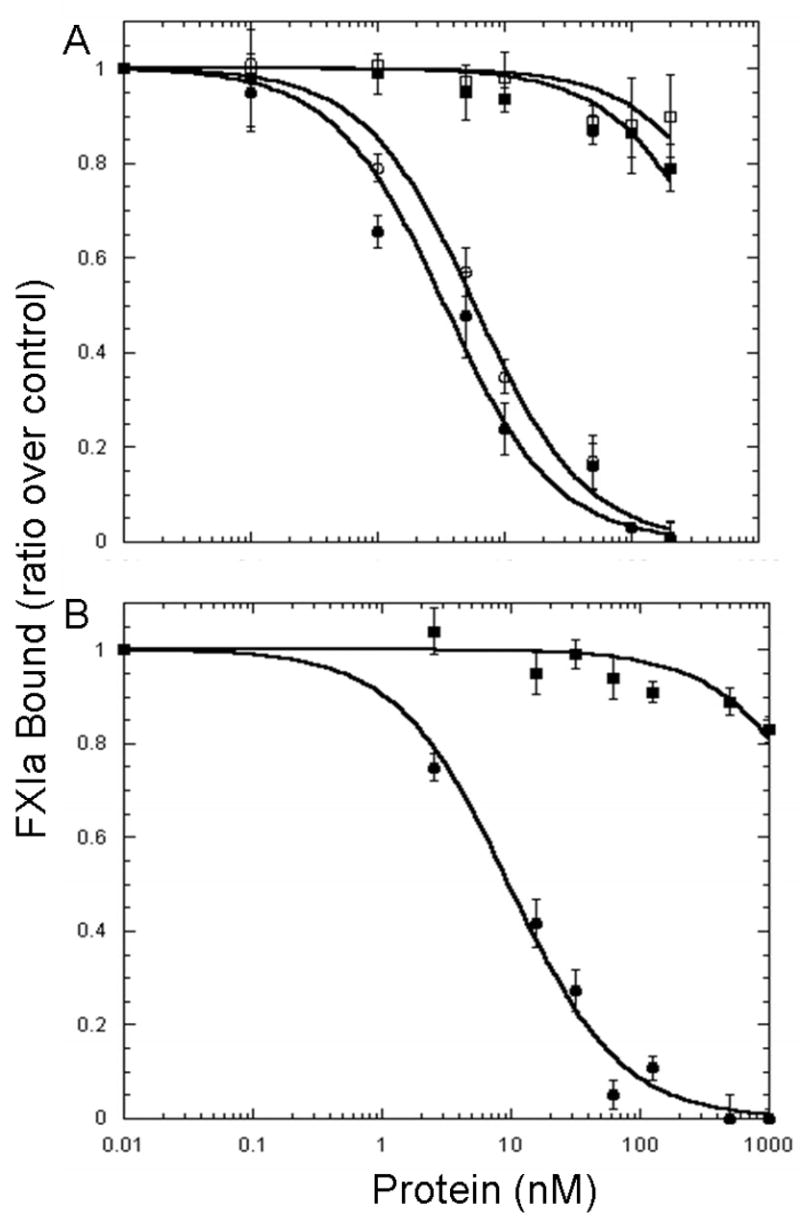
125I-FXIa (2 nM) was incubated with platelets (1 × 108platelets/ml), TRAP (25 μM) in the presence of CaCl2 (2 mM) and ZnCl2 (25 μM), and various concentrations of non-radiolabeled protein for 30 min prior to centrifugation through silicone oil. A, FXI (■) and rFXI/PKA3 (□) were unable to displace 125I-FXIa from the activated platelet surface whereas both FXIa (●) and rFXIa/PKA3 (○) were able to inhibit 125I-FXIa binding with Ki values of 1.4 ± 0.28 nM and 2.7 ± 0.32 nM respectively. B, The heavy chain (■) was unable to compete with 125I-FXIa for sites on the activated platelet whereas the catalytic domain (●) was effective in competing with 125I-FXIa for binding sites on the activated platelet surface with a Kiof 3.5 ± 0.42 nM. Values represent the mean ± standard deviation of three determinations each done in triplicate.
