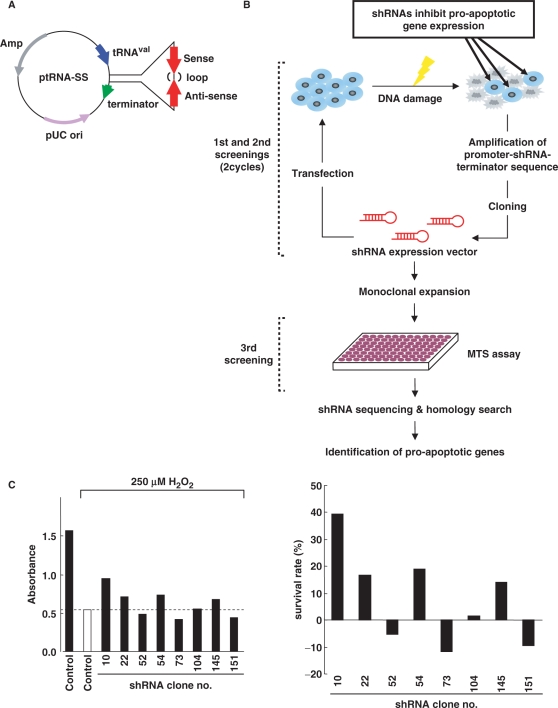
Figure 1.
shRNA library screen for pro-apoptotic genes. (A) Construction of shRNA expression library. The ptRNA-SS vector contains a tRNAval promoter and terminator in the pUC19 backbone, including ampicillin-resistance markers. The shRNA consists of a target transcript-specific 25–35 base double-stranded stem, connected by a 6-base loop sequence. (B) A schematic diagram of screening for identifying pro-apoptotic genes. 293T, HeLa or MCF-7 cells transfected with shRNA expression libraries (8 µg) were treated with H2O2 (200 µM for 293T and HeLa cells, and 500 µM for MCF-7 cells) or etoposide (100 µM for 293T cells, and 50 µM for HeLa cells) for 24 h. Adherent cells, judged as survived, were harvested, and total genomic DNA were isolated. The promoter-shRNA-terminator region was amplified from total genomic DNA. PCR products were digested by SphI and EcoRI, then ligated into pUC19. This process was repeated, and then the selected shRNAs were monoclonally expanded. Cells were plated on 96-well dishes and transfected with each of the shRNA clones, followed by treatment with H2O2 or etoposide for 24 h. MTS assays were performed to detect surviving cells. Sequencing of shRNA regions was carried out to identify putative target genes by homology search with BLAST. (C) MCF-7 cells transfected with individual shRNA clones were treated with 250 µM H2O2 for 24 h. MTS assays were performed to detect cells escaped from apoptosis. Absorbance obtained from cells transfected with pEGFP-C1 vector was determined as a control (left panel; open bar). Cells showing higher absorbance than the control value were selected as positive clones. A closed bar represents the value for untreated cells transfected with the empty vector (left panel). Survival rates were defined by calculating the absorbance obtained from the control cells with or without treatment, as 0 or 100%, respectively (right panel).