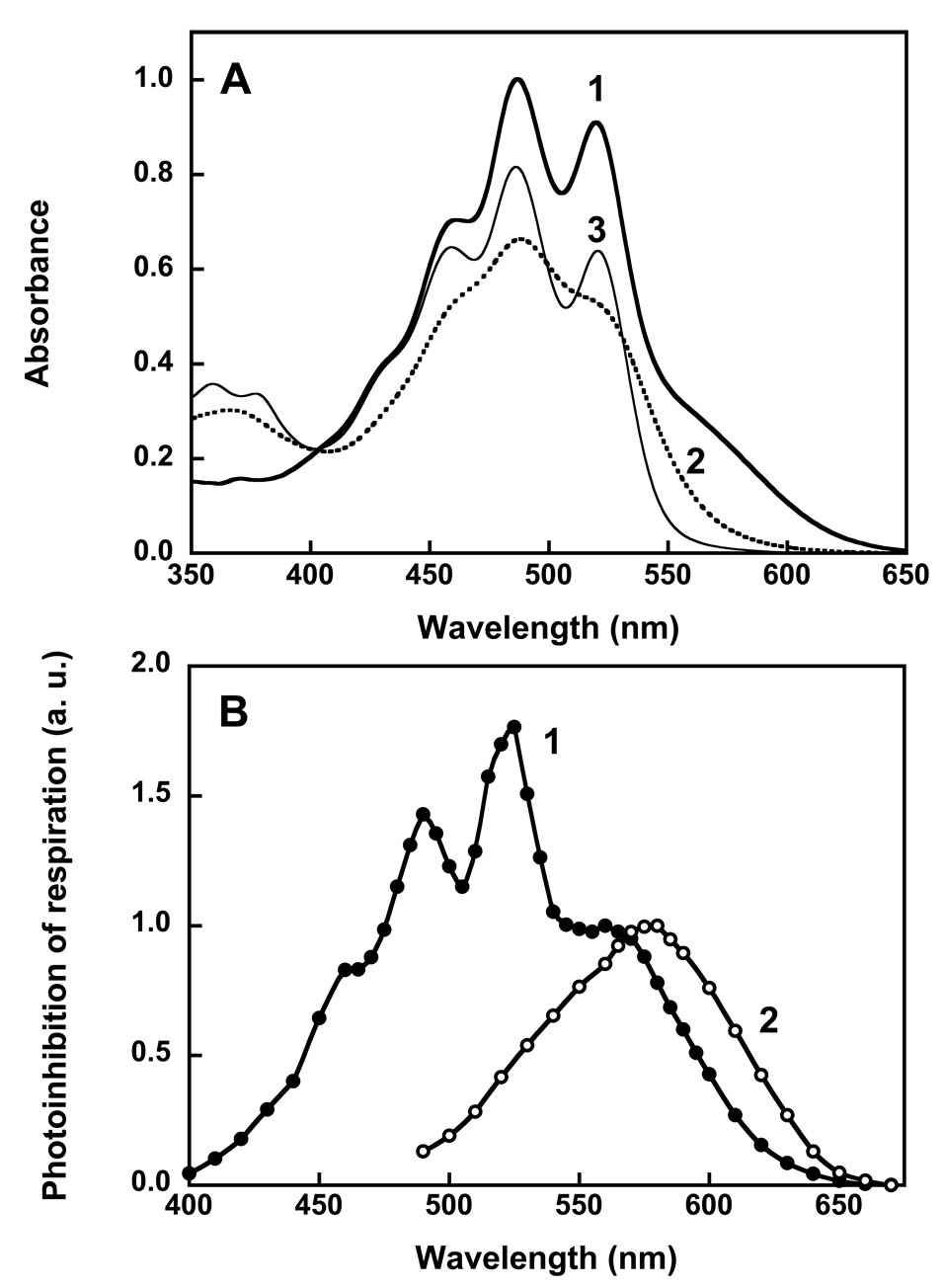
Fig. 1.
Absorption spectra (A) and action spectra (B) of xanthorhodopsin. In A: spectrum 1, xanthorhodopsin; spectrum 2, after hydrolysis of the retinal Schiff base with hydroxylamine; spectrum 3, after borohydride reduction of the retinal Schiff base. Hydroxylamine releases the retinal and that decreases the resolution of the vibronic bands of the carotenoid, while borohydride leaves the reduced retinal in its binding site and does not significantly alter the carotenoid spectrum. In B: spectra 1 and 2, action spectra for photoinhibition of respiration by S. ruber and Archaebacterium sp. (Halorubrum sp.) cells, respectively. After [13, 22, 25].