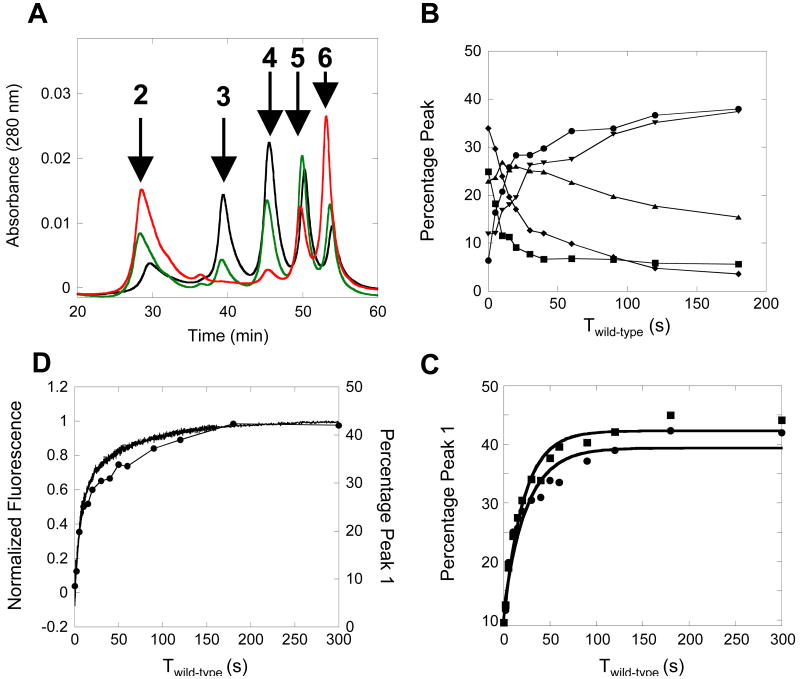
Figure 5.
TTR homotetramer reassembly can be monitored by a subunit incorporation assay. A) Anion exchange chromatogram of tetramers 2-6 after allowing the wild-type TTR (4.32 µM; monomer) to reassemble in the absence of flag-tag wild-type TTR for varying times (0 sec – black; 10 sec – green; 180 sec – red). Tetramers 2-6 (arrows) have different wild-type and flag-tag wild-type TTR subunit stoichiometries (tetramer 2 – (wild-type TTR)4 ; tetramer 3 (wild-type TTR)3 (flag-tag wild-type TTR)1 ; tetramer 4 (wild-type TTR)2 (flag-tag wild-type TTR)2 ; tetramer 5 (wild-type TTR)1 (flag-tag wild-type TTR)3 ; tetramer 6 (flag-tag wild-type TTR)4. B) Graph of the time dependent distribution of tetramers 2-6 as a function of the incubation time of wild-type TTR reassembly prior to the addition of flag-tag wild-type TTR (twild-type). Tetramer 2 – black circles ; Tetramer 3 – red squares ; Tetramer 4 – green diamonds ; Tetramer 5 – blue triangles ; Tetramer 6 – orange upside down triangles. C) Overlay of TTR homotetramer reassembly time courses (4.32 µM; monomer) as measured by the fluorescence of 1 (black line) and by the subunit incorporation method (black circles). The nearly identical kinetics strongly suggests that subunit incorporation measures the same kinetic process as the ligand binding fluorescence assay. D) Graph of TTR tetramer reassembly (4.32 µM; monomer) as measured by subunit incorporation in the presence (red squares) or absence (black circles) of small molecule 1. The similar time courses demonstrate that the small molecule does not interfere with the reassembly kinetics of TTR homotetramers.