Figure 3.
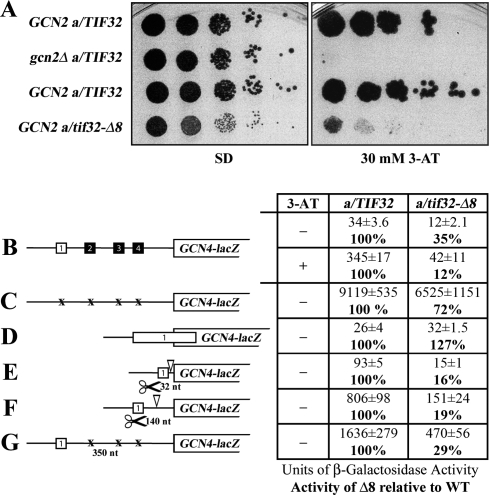
Evidence that a/tif32-Δ8 severely interferes with the reinitiation process by preventing post-termination retention of the 40S ribosome on mRNA. (A) a/tif32-Δ8 imparts a severe Gcn− phenotype implicating eIF3 in regulation of translational control of GCN4 expression that occurs via REI. Isogenic strains H2880 (GCN2 a/TIF32; row 1), and H2881 (gcn2Δ a/TIF32; row 2), YBS47 (GCN2 a/tif32Δ pRSeIF3a-His; row 3), YBS53 (GCN2 a/tif32Δ pRSeIF3a-Δ8-His; row 4), respectively, were spotted in five serial dilutions on SD (left panel) or SD containing 30 mM 3-AT (right panel) and then incubated for 3 and 7 d at 30°C, respectively. (B) a/tif32-Δ8 reduces basal expression of GCN4-lacZ and prevents its full derepression upon starvation. Isogenic strains YBS47 (a/TIF32) and YBS53 (a/tif32-Δ8) were transformed with p180, grown in minimal media for 6 and 8 h, respectively, and the β-galactosidase activities were measured in the WCEs and expressed in units of nanomoles of o-nitrophenyl-b-D-galactopyranoside hydrolyzed per minute per milligram of protein. To induce GCN4-lacZ expression, a/TIF32 and a/tif32-Δ8 transformants grown at the minimal media for 2 h were treated with 10 mM 3-AT for 6 or 16 h, respectively. The mean values and standard deviations obtained from at least six independent measurements with three independent transformants, and activity in a/tif32-Δ8 relative to wild type, respectively, are given in the table to the left of schematics. (C,D) The failure of a/tif32-Δ8 to derepress GCN4-lacZ is not caused by leaky scanning. YBS47 and YBS53 were transformed with p227 (C) and pM226 (D), respectively, and analyzed as in B, except that they were not treated with 3-AT. (E–G) The failure of a/tif32-Δ8 to derepress GCN4-lacZ is not caused by slow or defective scanning. YBS47 and YBS53 were transformed with pG67 (E), pM199 (F), or p209 (G), respectively, and analyzed as in C and D.