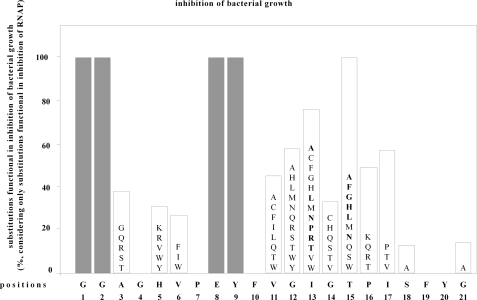
FIGURE 3.
Effects of single-amino acid substitutions in MccJ25 mutants on permeation into bacterial cells and inhibition of bacterial growth. Data are presented for 155 single-amino acid substitution derivatives of MccJ25, comprising all substitutions shown to be competent for production/maturation/export/stability and competent for inhibition of RNAP (see Figs. 1 and 2). The sequence of MccJ25 is shown at the bottom. The heights of bars indicate the percentage of tested amino acid substitutions that do not prevent permeation into bacterial cells and inhibition of bacterial growth. Letters within bars list amino acid substitutions that do not prevent permeation into bacterial cells and inhibition of bacterial growth. Letters in boldface type denote amino acid substitutions that result in apparent inhibitory activities higher than that of wild-type MccJ25. (Positions 1, 2, 8, and 9 (gray bars) were not analyzed, since no single-amino acid substitution derivatives at these positions were shown to be competent for production/maturation/export/stability and competent for inhibition of RNAP (see Figs. 1 and 2).)