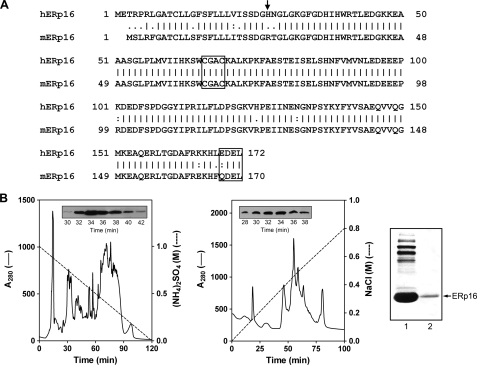
FIGURE 1.
Primary structure of ERp16 and its purification from mouse liver. A, alignment of the amino acid sequences of human (h) and mouse (m) ERp16. The NH2-terminal residue of the mature protein is indicated with an arrow. The active site sequence (CGAC) and ER retention motif (EDEL or QDEL) are boxed. B, purification of ERp16 from an ER-enriched fraction of mouse liver. ER proteins were subjected to sequential HPLC on Phenyl-5PW (left) and Mono-Q HR (middle) columns as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Insets, immunoblot analysis of column fractions with antibodies to ERp16. Peak fractions (numbers 32-34) from the Mono-Q HR column were pooled. Proteins in the pooled fraction (right, first lane) and recombinant mature human ERp16 (right, second lane) were subjected to SDS-PAGE on an 8% gel, transferred to a polyvinylidene difluoride membrane, and stained with Ponceau S. The mouse protein that migrated at the same position as recombinant ERp16 (arrow) was excised from the gel and subjected to NH2-terminal sequencing.