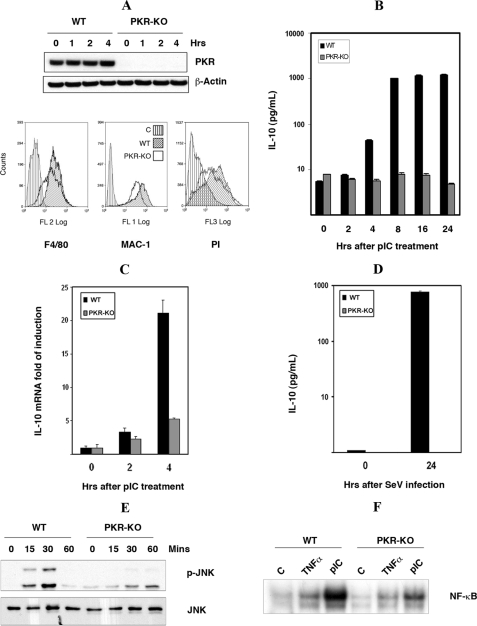
FIGURE 4.
The induction of IL-10 by dsRNA is PKR-dependent. A, characterization of wt and pkr-ko SM cells, by Western blot analysis with an antibody to PKR (upper panel), flow cytometric analysis with antibodies detecting macrophage markers (F4/80 and MAC-1), and phagocytic assay measuring uptake of PI (lower panel). Only the wt SM control cell line is shown in each graph, as the pkr-ko control was equivalent. The control (C) in each graph was either without antibody or incubated at low temperature to inhibit phagocytosis. B, induction of IL-10 by dsRNA was measured in wt and pkr-ko SM cells treated with pIC (50 μg/ml) for the indicated time periods and assessed by ELISA for IL-10 protein levels. C, to assess the requirement for PKR in an alternative cell system, wt and pkr-ko primary BMM were treated with pIC (50 μg/ml) for indicated times, total RNA was extracted, and IL-10 mRNA was measured by real-time quantitative PCR. D, to validate the dsRNA response with a biologically pertinent stimulus, wt and pkr-ko SM cells were infected with Sendai virus (SeV) at a concentration of 80 HAU for 24 h and the level of IL-10 protein in the cell supernatants measured by ELISA. The experiment was done in triplicate. In keeping with the previous data showing a role for JNK and NF-κB in dsRNA-mediated IL-10 induction: E, PKR-dependent activation of JNK was measured in wt and pkr-ko SM cells treated with pIC (50 μg/ml) for indicated times, by Western blot using the phospho-JNK (p-JNK) antibody. Total JNK level was measured to verify equal loading. F, PKR-dependent activation of NF-κB was measured by EMSA in cell lysates from wt and pkr-ko SM cells, either untreated (C), treated with pIC (50 μg/ml), or as a control TNFα (25 ng/ml) for 30 min.