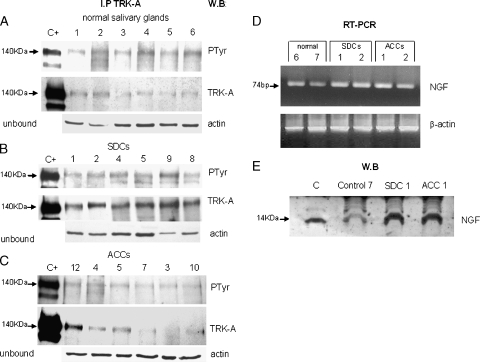
Figure 1.
TRK-A expression and activation. For each sample, total protein extracts were immunoprecipitated with α-TRK-A antibody, run on gel, and blotted with α-PTyr antibody (PTyr panel) for receptor phosphorylation status and with α-TRK-A antibody (TRK-A panel) for receptor expression. Normalization of the experiment was done using 50 µg of unbound proteins and blot analysis with α-actin antibody (actin panel). Lane C+: positive control (E25 cell line). Lane numbers correspond to the cases reported in Table 1. (A) Expression of TRK-A and its phosphorylation in six normal salivary glands. (B) Expression of TRK-A and its phosphorylation in six overexpressing SDC cases. (C) Expression of TRK-A and its phosphorylation in six ACC cases. (D) Expression detected by RT-PCR experiments of NGF transcript in normal and tumoral salivary glands. A total of 1 µl of cDNA was used as template for each NGF and β-actin gene amplification reaction; 10 µl of PCR were loaded on 2% agarose gel. (E) Expression of NGF in normal and tumoral salivary glands. A total of 50 µg of protein lysate was loaded onto a 15% acrylamide gel and blotted with α-NGF antibody. Lane C: positive control (NGF 2.5 S).