Figure 2.
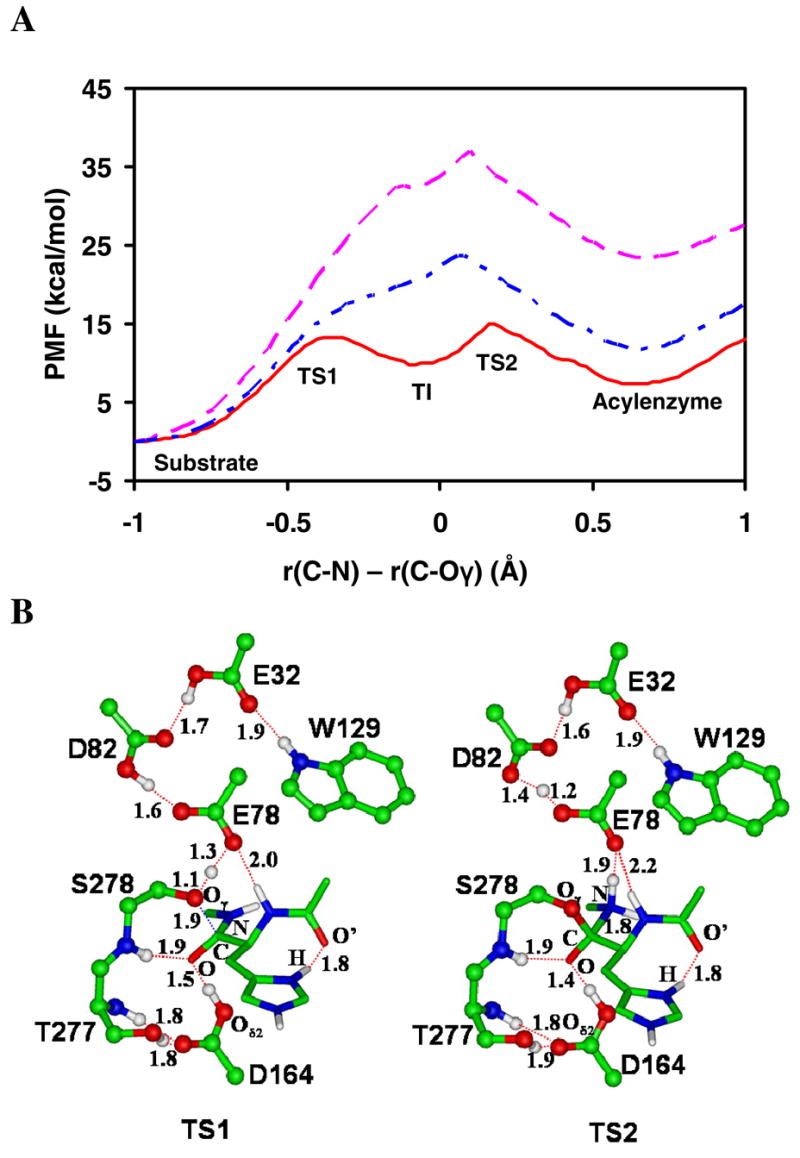
(A) The free energy profiles of the acylation reaction for the wild-type kumamolisin-As and D164A mutant as a function of the reaction coordinate [ζ = R(C-N) - R(C…Oγ)] obtained from the QM/MM free energy (potential of mean force) simulations. Red solid line: wild-type; blue dot-dashed line: wild-type with the proton fixed on Asp164 with the SHAKE algorithm; pink dashed line: D164A. The average structures for the substrate complex, tetrahedral intermediate and acyl-enzyme for wild-type are given in Figure 1A, 1C and 1E, respectively. The average structures of TS1 and TS2 for wild-type are given in Figure 2B. (B)The average active-site structures for wild-type near the transition states for the nucleophilic attack (TS1) and the formation of the acyl-enzyme (TS2), respectively, obtained from the free energy simulations.
