Figure 3.
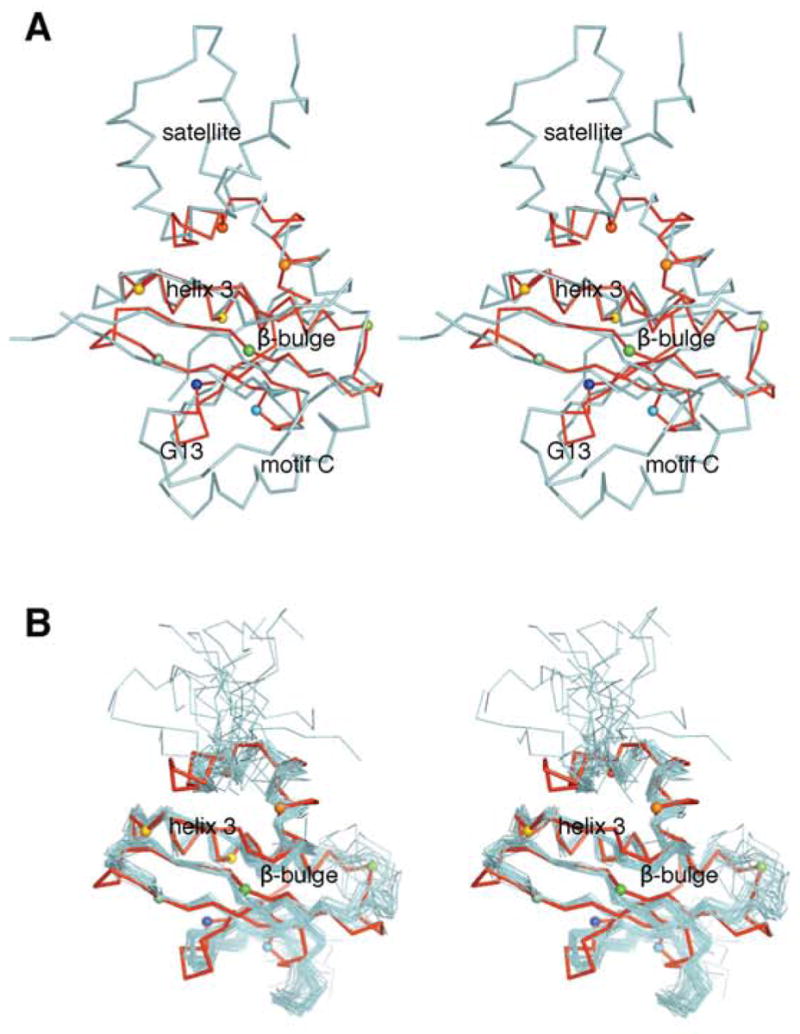
Structural alignment of At1g77540 with (A) Hat1. Stereo diagram showing the aligned structural models for At1g77540 (red; PDB # 1xmt, this study) and histone acetyltransferase Hat1 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae (cyan; residues 122–300; PDB # 1bob). (B) COG2388 family member 1r57. Stereoscopic diagram showing the aligned structural models for At1g77540 (red; PDB #1xmt) and closest structural COG2388 family member from Staphylococcus aureus (PDB # 1r57). The view is rotated approximately 90° clockwise compared to that in Figure 1. Selected Cα atoms are highlighted by spheres, with colors consistent with those used in Figure 1C. At1g77540 contain only a minimal acetyltransferase fold with the conserved “signature” helix 3, central β-sheet containing functionally important β-bulge, and the CoA-binding loop (residues 43–53). Important structural features present in Hat1 but not present in At1g77540 include 1) motif C, which forms a helix that runs perpendicular to the β-strands of the central β-sheet; 2) the independent amino-terminal domain of Hat1 (residues 1–121 of Hat 1, not shown); 3) the helix-bundle-like satellite domain at the carboxyl-terminus of Hat1.
