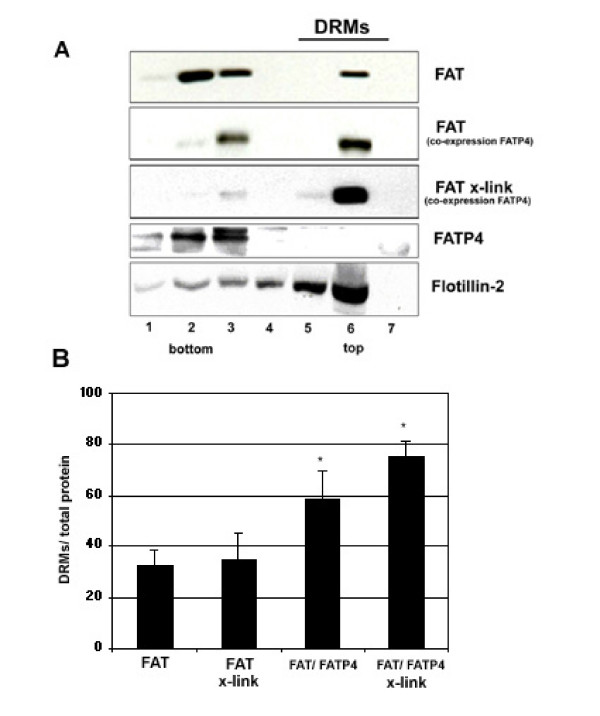
Figure 5.
Effect of antibody cross-linking on association of FAT/CD36 to DRMs. 20 h after transient transfection of FAT/CD36, FATP4 or both COS cells were were lysed in 1% Triton X-100/TNE at 4°C. (A) After floatation in an OptiPrep step-gradient FAT/CD36 was found in two pools, in DRMs and in soluble membranes (lane 1–3). Co-expression of FATP4 resulted in an increased relative amount of FAT/CD36 found in DRMs (lane 6). Antibody cross-linking of FAT/CD36 using an mouse anti human FAT/CD36 antibody from Biosource shifted FAT/CD36 towards the DRM fractions (lane 6). No significant amount of FATP4 was found in DRMs, indicating that FAT/CD36 and FATP4 might be in distinct compartments within the cell. Flotillin-2, a typical raft protein was used as a control to estimate the quality of DRM isolation. The results are representative of three others experiments carried out independently. (B) Quantification; FATP4 expression and antibody-induced patching significantly increased the amount of FAT/CD36 in the top two fractions (DRM associated). The amount in the top two fractions was correlated to the total amount of protein in all fractions. Data are expressed as mean and SEM of n = 3 experiments. Asterisk indicates significant differences to cells transfected with FAT/CD36 only (p < 0.05).