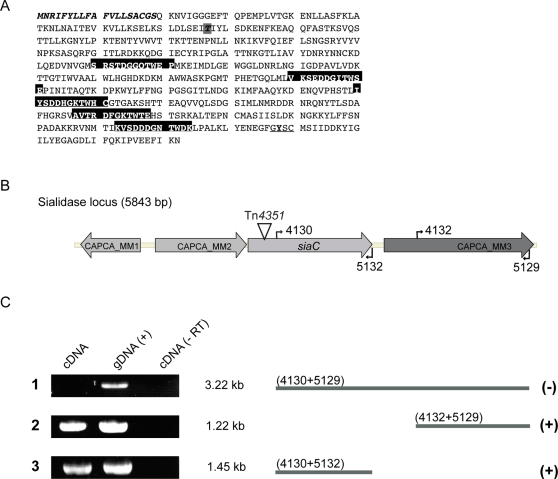
Figure 2. Identification of the Tn integration site and analysis of mRNA present in wt C. canimorsus 5.
(A) Amino acid sequence of the C. canimorsus sialidase showing the signal peptide (italics) and the BNR/asp repeats (Ser/Thr-X-Asp-X-Gly-X-Thr-Trp/Phe) of bacterial sialidases (boxed). Domain predictions were analyzed by InterProScan [42]. The residues conserved in sialidases at the C-terminus are underlined and the tyrosine 488 is bold [43]. The Tn4351 integration site in SiaC at amino acid 77 is indicated, boxed in grey and bold. (B) Genetic locus of the sialidase gene (siaC) including its upstream genes, gntR-like gene (CAPCA_MM1) and putative N-acyl-glucosamine epimerase encoding gene (CAPCA_MM2); and downstream coding sequence (CAPCA_MM3). (C) Reverse transcription performed on total RNA with specific primers (5129 or 5132) followed by PCR to identify transcripts present in wt Cc5 (cDNA). PCR reactions were also performed using genomic DNA (gDNA) as template instead of cDNA as a positive control. As a control, reverse transcription was performed without reverse transcriptase in a parallel assay and used as template for the subsequent PCR reaction (-RT).