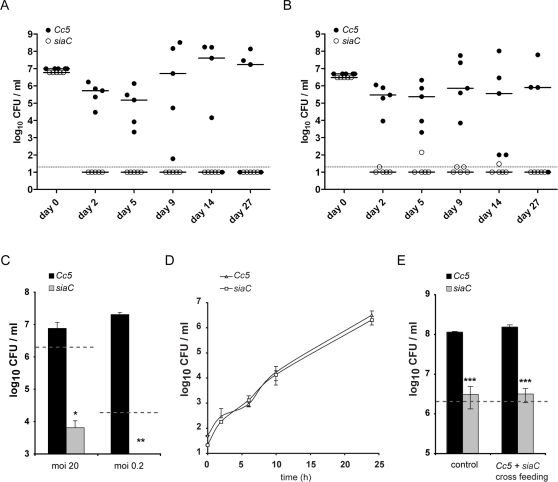
Figure 7. The sialidase mutant is hypo-virulent in a tissue cage mouse infection model.
Tissue cages were implanted in C57BL/6 mice and infected with 107 Cc5 wt and siaC bacteria (n = 5) singly (A) or in competition (B). Bacteria were counted in tissue cage fluid (TCF) during 27 days (Cc5 = black circles; siaC = open circles). Individual values are shown; horizontal lines indicate the median value of each group. The black dotted line is the detection limit of 20 bacteria per ml TCF. (A) Cfu numbers between groups were significantly different on days 2, 5 and 9 with p<0.01 and on days 14 and 27 with p<0.05 (Mann Whitney test). (B) 107 cfu Cc5 and erythromycin resistant siaC were inoculated at a 1∶1 ratio. Bacterial numbers were analyzed for 27 days (n = 5). Viable counts between wt and siaC were significantly different on day 2, 5 and 9 with p<0.01 and on day 14 with p<0.05. (C) Ex vivo isolated leukocytes were resuspended in serum free RPMI and inoculated at a moi of 20 (2×106 bacteria) or 0.2 (2×104 bacteria) indicated with grey dotted lines and bacterial viable count was monitored after 24 h. Values represent the mean using TCF cells from 3 uninfected mice. TCF leukocytes consist of 68% +/− 4.8% polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMNs), 18% +/− 3.2% monocytes and 9.1% +/− 3.7% macrophages. Wt and siaC numbers were significantly different with p<0.05 (*) and p<0.001 (**) using 2-tailed unpaired student's t test. (D) In vitro, Cc5 and siaC were tested in heart infusion broth with FBS inoculated at a 1∶1 ratio with approximately 100 bacteria total and bacterial growth was monitored for 2, 6, 10 and 24 h. (E) Viable counts after challenge with 2×106 (grey dotted line) Cc5 (black) or siaC (grey) grown for 24 h with J774.1 in cRPMI singly (control) or at a 1∶1 ratio (cross-feeding).