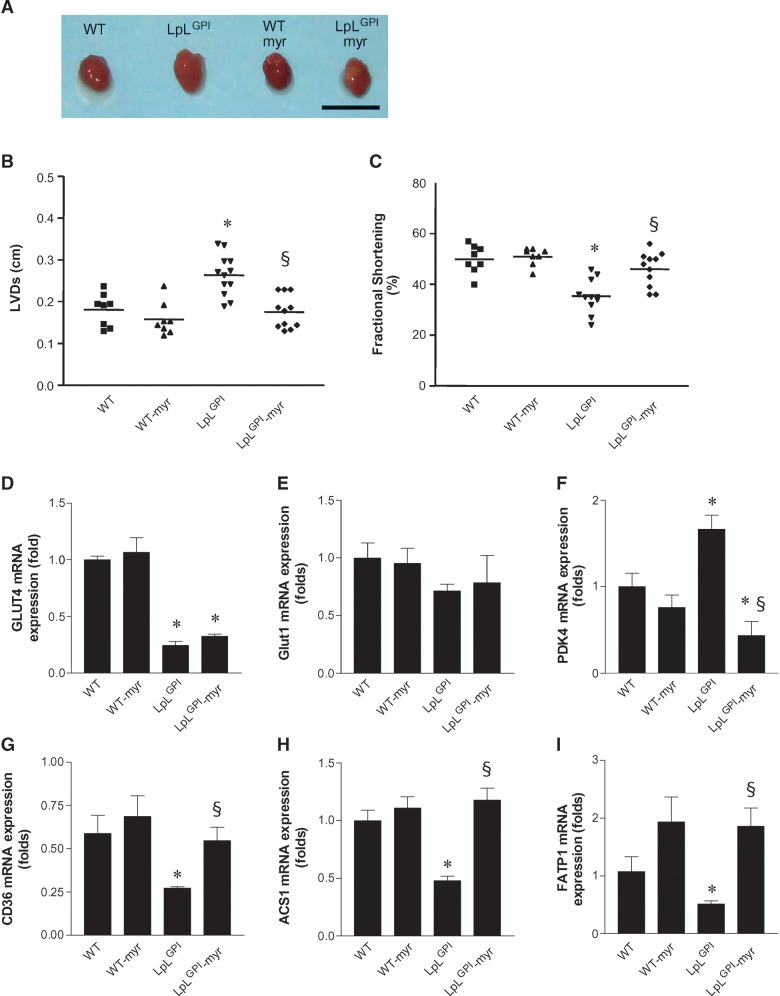
Fig. 1.
Prevention of cardiomyopathy by myriocin in glycosylphosphotidylinositol (GPI)-anchored human lipoprotein lipase (LpLGPI) hearts and regulation of cardiac gene expression in LpLGPI mice. Eight week-old wild-type (WT) and LpLGPI mice were fed chow or chow with 0.3 mg myriocin/kg/day for 6 weeks. Hearts from mice are shown (A). Chow-fed LpLGPI mouse hearts were enlarged, but hearts from LpLGPI mice fed myriocin-mixed chow were normal size. Left ventricular systolic diameter (LVD) (B) of the heart and fractional shortening (C) were measured by echocardiography as described in Materials and Methods (n = 8–12 each group). mRNA expression in the heart was measured by RT-PCR as described in Materials and Methods. Glucose-metabolizing genes GLUT4 (D), GLUT1 (E), and PDK4 (F). FA transporters CD36 (G), ACS1 (H), and FATP1 (I). Bar indicates 1 cm. *P < 0.05 versus WT; §P < 0.05 versus LpLGPI.