Fig. 4.
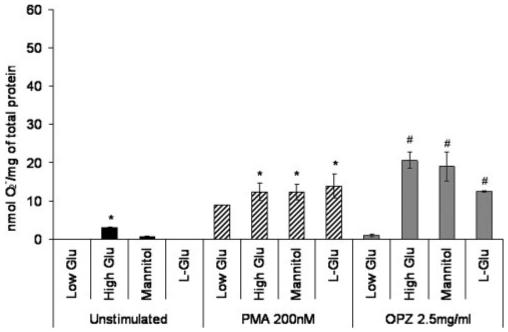
Effects of high glucose concentration and hyperosmolarity on O2- generation from normal human mononuclear phagocytes, which were isolated from healthy controls (n=4) and cultured in RPMI 1640 with low glucose (5.5 mM D-glucose), high glucose (25.5 mM D-glucose), mannitol (5 mM D-glucose, 20 mM mannitol), or L-glucose (5.5 mM D-glucose, 20 mM L-glucose). The cells were assayed after 2 days for O2- anion generation in the resting state or under stimulation with PMA or OPZ. The amount of O2- production was adjusted by total protein content of each well (nmol O2-/mg total protein). All values represent the average ± se (*, P<0.05, compared with low glucose; #, P<0.01, compared with low glucose).
