Table 1.
Addition of silylketene acetal 27 to aldehydes 28a and 28b.
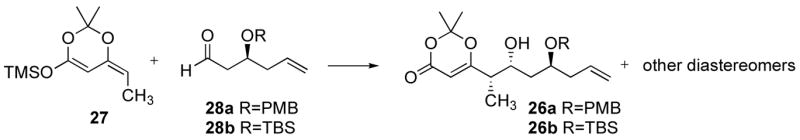 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| entry | R | E/Z-ratio 27 | lewis acid | solvent | 2,4-anti/syna | 1,2-anti/synb | yieldc |
| 1 | TBS | 1.6:1 | TiCl4 | CH2Cl2 | - | - | decomp. |
| 2 | TBS | 1.6:1 | BF3·OEt2 | CH2Cl2 | 2:1 | 1:1 | 78 % |
| 3d | PMB | 1.6:1 | TiCl4 | CH2Cl2 | 2.6:1 | 1:4e | 61 % |
| 4 | PMB | 1.6:1 | BF3·OEt2 | CH2Cl2 | 1.7:1 | 1:1 | 76 % |
| 5 | PMB | 1.6:1 | TiCl2(OiPr)2 | CH2Cl2 | 3.4:1 | 1:1.3 | 80 % |
| 6 | PMB | 1.6:1 | TiCl2(OiPr)2 | toluene | 7.5:1 | 1:1 | 89 % |
| 7 | PMB | 10:1 | TiCl2(OiPr)2 | CH2Cl2 | 3:1 | 2:1 | 75 % |
| 8 | PMB | 10:1 | TiCl2(OiPr)2 | toluene | 8:1 | 3:1 | 73 % |
| 9 | PMB | 1:2 | TiCl2(OiPr)2 | CH2Cl2 | 4:1 | 1:1.4 | 80 % |
| 10 | PMB | 1:2 | TiCl2(OiPr)2 | toluene | 5:1 | 1.1:1 | 72 % |
All four diastereomers were inseparable; the ratio was determined by integration of the PMB benzylic protons, which gave one AB system for each pair of 2,4-anti and 2,4-syn diastereomers.
Determined by integration of the protons of the methyl α to the hydroxyl, which gave one doublet for each pair of 1,2-anti and 1,2-syn diastereomers.
Combined yield of all diastereomers.
Loss of the PMB group was observed.
The 2,4-anti/syn diastereomers were separable; the 1,2-anti/syn ratio is given for the desired 2,4-anti product.
