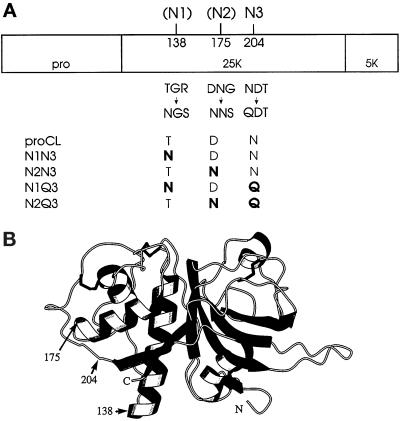
Figure 1.
Representations of (pro)cathepsin L. (A) Linear map of proCL showing the profragment (pro) and both segments of the mature enzyme (25K + 5K). On top of the map are the amino acid positions of the glycosylation sites used in this study: 204,N3 is the single wild-type site in human proCL; 138 (N1) and 175 (N2) are two novel sites introduced in this work. Directly below the map are the wild-type sequences at residues 138–140, 175–177, and 204–206 and the mutations at those residues that either create (138 and 175) or destroy (204) glycosylation signals. The bottom of the panel shows the names of the relevant mutants and their corresponding amino acids encoded at positions 138, 175, and 204, with mutations shown in boldface. (B) Drawing of a three-dimensional computer model of cathepsin L. The model was developed as described in MATERIALS AND METHODS. Numbers and arrows designate the positions of amino acids relevant to this study.