Figure 1.
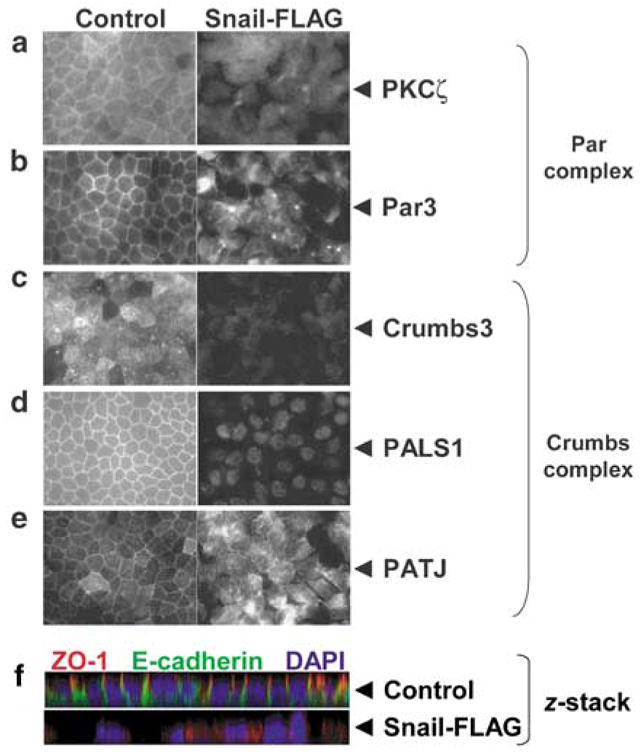
Snail expression disrupts junctional localization of the Crumbs and Par complexes and apico-basal polarity. A retroviral construct containing human Snail cDNA with a FLAG-epitope tag has been previously described (Hajra et al., 2002). Stable Madin–Darby Canine Kidney (MDCK) cell lines were created by retroviral mediated gene transfer and selected with 600 μg ml−1 G418 (Whiteman et al., 2003). Control and Snail-FLAG MDCK cells were grown on 24 mm Transwell filters (0.4 μm pore size; Corning Inc., Corning, NY, USA) for at least 72 h to achieve a tightly packed monolayer. The filters were immunostained for the indicated markers and images were captured as described (Straight et al., 2006). (a and b) Par complex: PKCζ and Par3 (tight junction), (c–e) Crumbs complex: Crumbs3, PALS1, PATJ (tight junction), (f) Confocal z-stack triple labeled for ZO-1 (tight junction), E-cadherin (adherens junction) and 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) (nuclei). The z-stack image was obtained using an Olympus FluoView 500 laser-scanning confocal microscope, and images were collected in 0.3 μm z-steps ( × 600). Antibodies used: polyclonal PKCζ (Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA); polyclonal Crumbs3, PALS1, PATJ and Par3 were previously described (Roh et al., 2002); monoclonal ZO-1, polyclonal E-cadherin, fluorochrome-conjugated secondary antibodies (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA).
