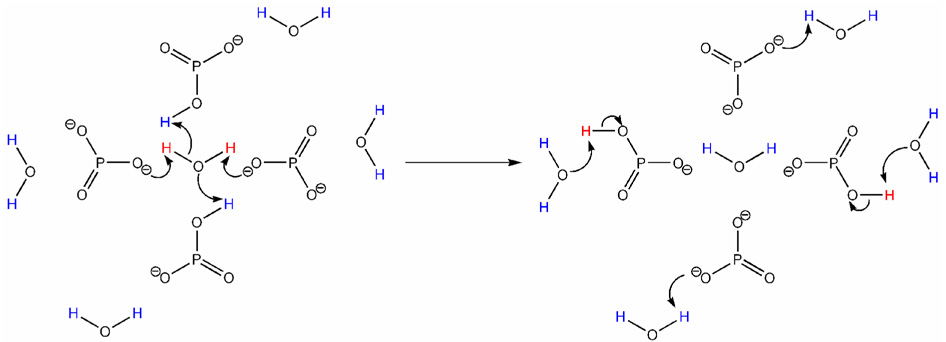
Figure 8.
A schematic representation, viewed down the Gd-OH2 axis, of how the phosphonates in GdLH23− transfer protons between the coordinated water molecule and the bulk solvent. The relaxed protons of the coordinated water molecule (shown in red) are removed from the water molecule by the deprotonated phosphonates which act as bases. They are then replaced by unrelaxed protons from the bulk water (shown in blue) which are supplied by the monoprotonated phosphonates which are acting as acids.