FIGURE 5.
Effects of PtdInsP depletion and induction and the mutation of
PtdInsP-binding site on kinetics of PM translocation of PKCα-C2.
A, the RFP intensity ratio (=PM/(PM + cytosol)) of PKCα-C2-RFP,
which indicates the relative abundance of the protein at PM versus
cytosol, is plotted as a function of time. The plots are shown for no lipid
depletion (•, Fig.
4C), PtdIns(4,5)P2 depletion (○,
Fig. 4D;
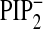 ), PtdIns(3,4,5)P3
depletion (Δ, Fig.
4E;
), PtdIns(3,4,5)P3
depletion (Δ, Fig.
4E; 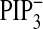 ), and
PtdIns(4,5)P2 + PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 depletion (□;
Fig. 4F;
), and
PtdIns(4,5)P2 + PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 depletion (□;
Fig. 4F;
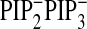 ).
B, the RFP intensity ratio as a function of time is shown for no
lipid induction (•, Fig.
4C), PtdIns(4,5)P2 induction (Δ,
Fig. 4H,
).
B, the RFP intensity ratio as a function of time is shown for no
lipid induction (•, Fig.
4C), PtdIns(4,5)P2 induction (Δ,
Fig. 4H,
 ), and PtdIns(3,4,5)P3
induction (○, Fig.
4G,
), and PtdIns(3,4,5)P3
induction (○, Fig.
4G, 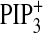 ).
C, the fluorescence intensity ratios of PKCα-C2-RFP (•)
and K209A/K211A (○) co-transfected into NIH-3T3 cells
(Fig. 4I) are plotted
as a function of time. No lipid depletion was performed for this
measurement.
).
C, the fluorescence intensity ratios of PKCα-C2-RFP (•)
and K209A/K211A (○) co-transfected into NIH-3T3 cells
(Fig. 4I) are plotted
as a function of time. No lipid depletion was performed for this
measurement.

