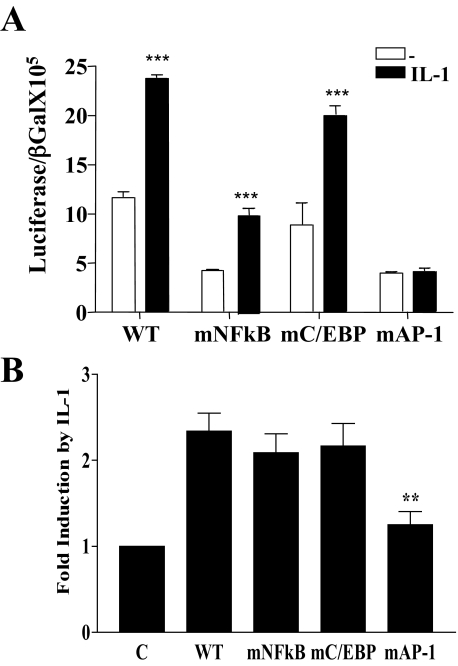
FIGURE 5.
Mutation of the consensus NFκB site affects baseline IL-6 promoter activity, whereas mutation of the AP-1 site significantly impairs its induction by IL-1. Caco-2 cells were transfected with the IL-6 promoter luciferase constructs (0.25 μg), pIL-6-luc651WT (WT), pIL-6-luc651 mutated in the NFκB binding site, pIL-6-luc651 (mNFκB), pIL-6-luc651 mutated in the consensus binding site for C/EBPβ, pIL-6-luc651 (mC/EBPβ), or pIL6–651 mutated in the AP-1 site, pIL-6-luc651 (mAP-1). A β-galactosidase reporter (0.25 μg) was included for transfection efficiency. Eighteen hours after transfection, cells were starved for 3 h and were either untreated or IL-1 treated (0.5 ng/ml) overnight. Lysates were assayed for luciferase and β-galactosidase. A, baseline and IL-1 stimulation of each construct with promoter activation expressed as the ratio of luciferase/β-galactosidase. Mean ± S.E. (n = 3). ***, p < 0.001, pIL-6-luc651WT and mutants, mNFκB, mC/EBP, untreated compared with IL-1 treated. B, -fold induction by IL-1 with untreated, control values set at 1, mean ± S.E. (n = 3). ***, p < 0.001, IL-6-651mAP-1 transfectants compared with pIL-6–651WT transfectants treated with IL-1.