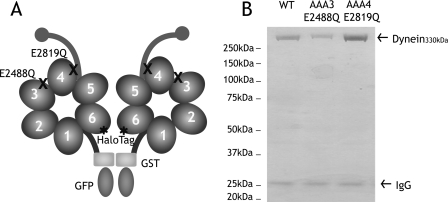
FIGURE 1.
Construction and purification of dynein ATP hydrolysis mutants. A, a minimal S. cerevisiae cytoplasmic dynein that demonstrates processive motility was engineered as described previously (17). A glutathione S-transferase tag (GST) was incorporated at the NH2 terminus for the dimerization of the two heads of cytoplasmic dynein, whereas a HaloTag was fused to the COOH terminus for fluorescent labeling of the heads. In this paper, this construct is referred to as “wild-type dynein.” Highly conserved glutamate residues in the Walker B motif of domains AAA3 (E2488) and AAA4 (E2819) were mutated to glutamine to block ATP hydrolysis. B, Coomassie Blue-stained polyacrylamide gel of recombinant cytoplasmic dynein purified from S. cerevisiae by affinity purification. 330-kDa recombinant dynein is purified with minor amounts of 26-kDa IgG from the affinity matrix. WT, wild type.