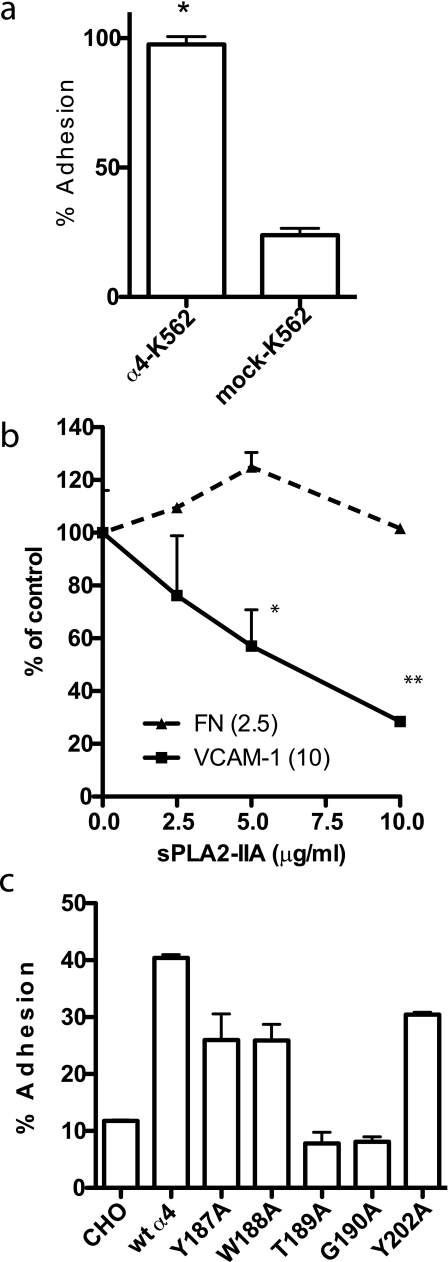
FIGURE 5.
sPLA2-IIA binding to integrin α4β1. a, cells expressing recombinant α4β1 adhered to Wt sPLA2-IIA better that cells expressing other recombinant integrins. We used transfected K562 cells clonally express different human integrins for adhesion assays. Low background adhesion to BSA was subtracted. Data are shown as means ± S.E. of triplicate experiments. b, sPLA2-IIA blocked adhesion of U937 cells to VCAM-1, but did not block adhesion of U937 cells to the cell-binding domain of fibronectin. Wells of 96-well microtiter plate were coated with VCAM-1 and FN-GST, and incubated with U937 cells (1 × 104 cells/plate) in the presence of the increasing concentrations of sPLA2-IIA for 1 h at 37 °C. Adherent cells were quantified using endogenous phosphatase after gently rinsing the well to remove unbound cells. Data are shown as means ± S.E. of triplicate experiments. *, p = 0.0101 and **, p < 0.0001 by Student's t test. c, amino acid sequence in the α4 subunit that is critical for VCAM-1 and CS-1 binding is also critical for sPLA2-IIA binding. CHO cells that clonally express Wt or mutant α4 (23) were used for adhesion assays. Data are shown as means ± S.E. of triplicate experiments. Similar results were obtained using K562 cells expressing α4 mutants (not shown).