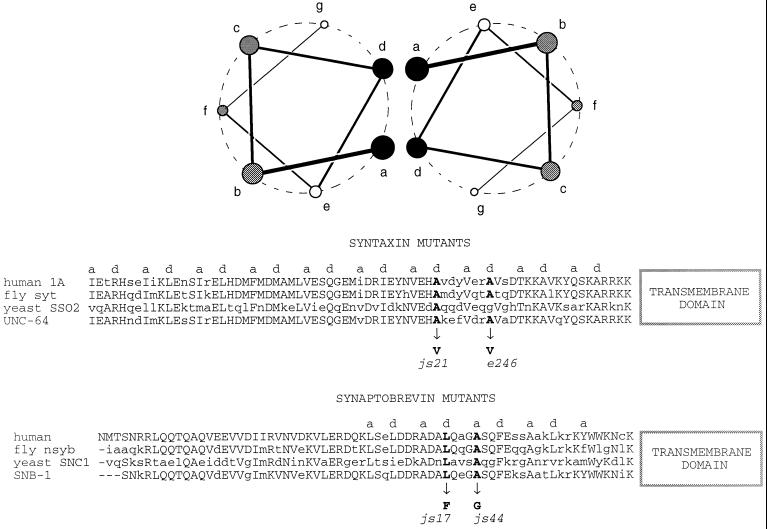
Figure 8.
Mutations in snb-1 and unc-64 on the hydrophobic faces of α-helices proposed to mediate interactions between synaptobrevin and syntaxin. Two model amphipathic α-helices composed of a repeating seven-amino acid pattern. The residues are labeled a through g. Residues in a and d positions are usually hydrophobic and are proposed to mediate interactions between binding partners. Below, a portion of the sequences of human, fly, yeast, and worm syntaxin and synaptobrevin (Archer et al., 1990; DiAntonio et al., 1993; Gerst et al., 1992) are aligned. Hydrophobic residues in the a and d positions of the predicted α-helices are labeled. The site of lesions in C. elegans syntaxin and synaptobrevin (Nonet et al., 1998) are also labeled. The two sequences are oriented assuming they will interact in a parallel manner (Hanson et al., 1997; Lin and Scheller, 1997).