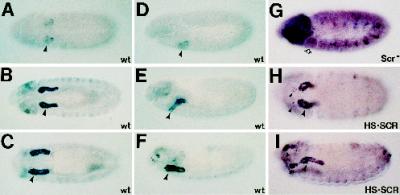
Figure 1.
Expression of enhancer traps in WRS-85D is observed at high levels in the salivary gland and is under the control of the homeotic gene Scr. Embryos have been immunostained with an mAb to β-gal. Embryos in A–C, and H are ventral views; embryos in D–G and I are lateral views. Embryos in A–F show staining dependent on the P-element insertion in the stock l(3)03559 in a wild-type genetic background. In addition to the high-level expression of β-gal in the salivary gland, we also detected expression in the head sensory sensilla that will form the dorsal and ventral organs (F) (Campos-Ortega and Hartenstein, 1997). (G) Immunostaining from the P-element stock in an embryo missing Scr function (an Scr4 homozygote). Note the loss of expression in the salivary gland primordia even when the embryo is significantly overstained to demonstrate both head and PNS staining. (H and I) β-Gal staining in an l(3)03559 embryo where SCR is expressed everywhere under the control of an induced heat-shock promoter (HS·SCR). Note the ectopic β-gal expression in ventrolateral cells of PS1 in H and in PS0, PS1, and PS14 in I. An identical profile of β-gal expression is observed in embryos carrying the l(3)04410 insertion (our unpublished results).