Abstract
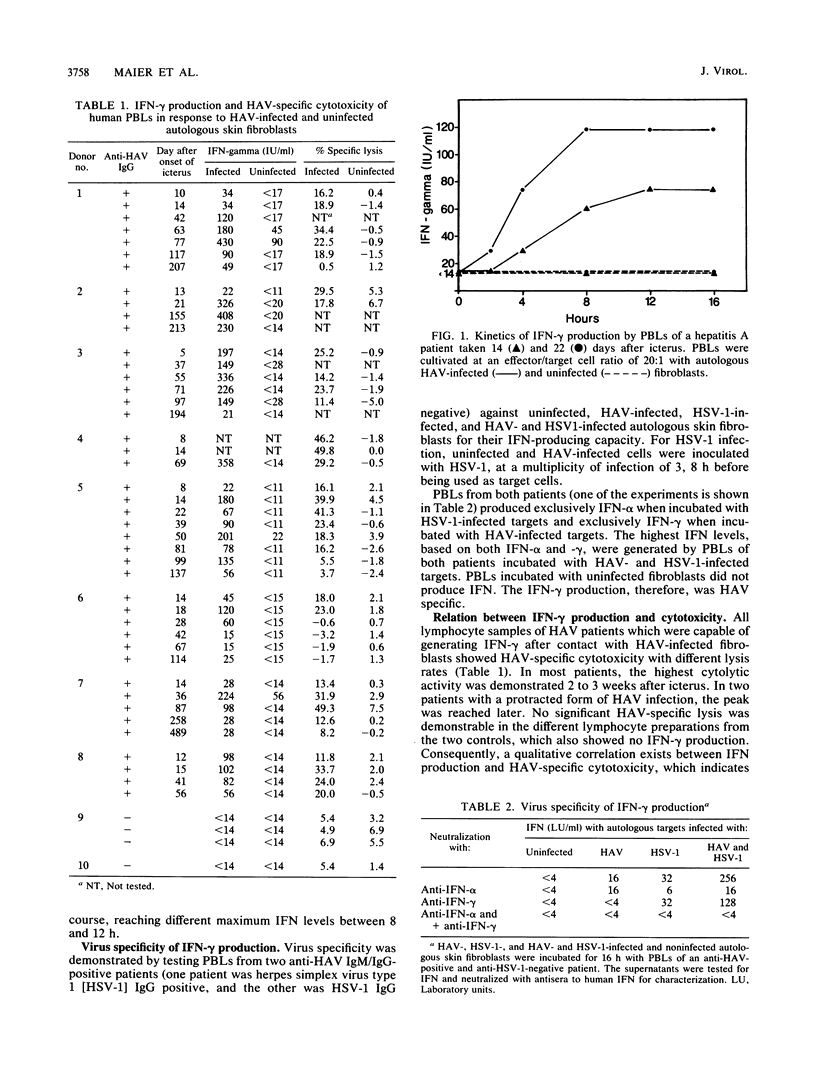
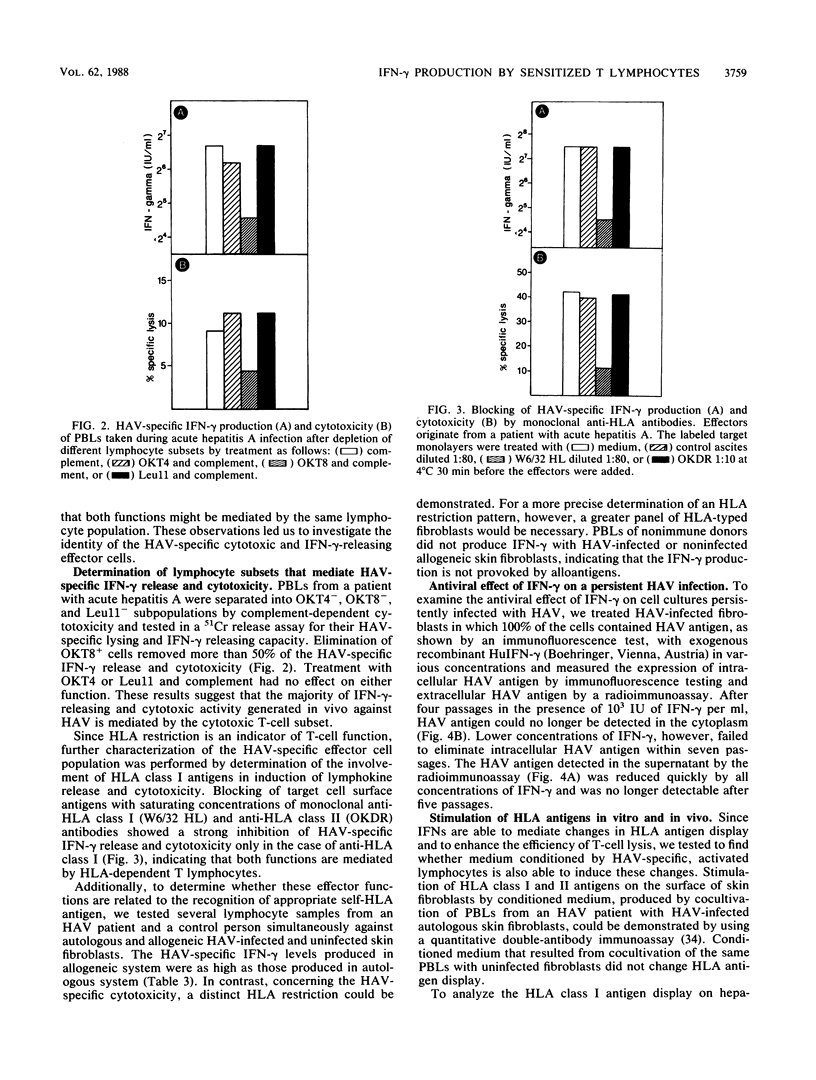
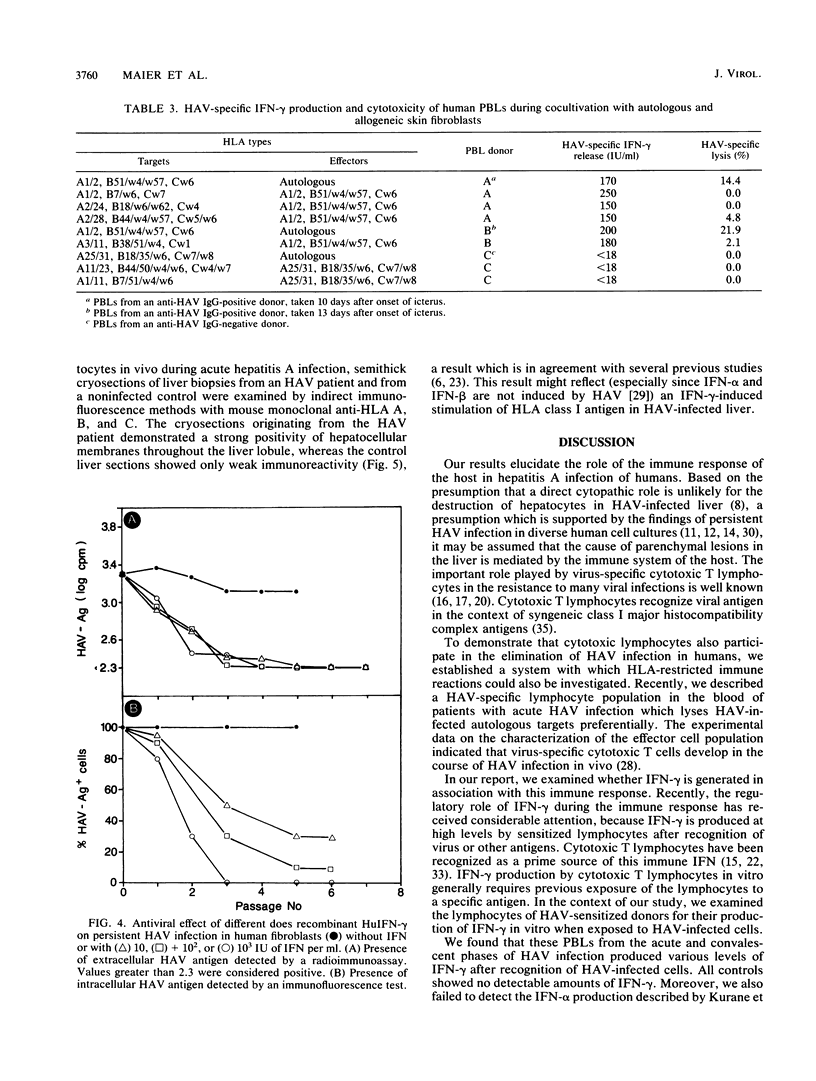
The production of interferon (IFN) during a chromium-51 release assay with hepatitis A virus (HAV)-infected fibroblasts and autologous peripheral blood lymphocytes from patients with acute HAV infection was studied to determine whether IFN plays a role in immunopathogenesis of hepatitis A infection in humans. Skin fibroblasts of eight patients after acute HAV infection and from two control persons without history of current or past HAV infection were infected with HAV. Peripheral blood lymphocytes were collected at different times after the onset of icterus and tested in a chromium-51 release assay against autologous HAV-infected skin fibroblasts for their cytolytic and IFN-producing activity. The IFN produced during the assay was characterized and found to have the properties of human gamma IFN. Cytotoxicity and gamma IFN release were virus specific. The cell types responsible for both functions were characterized and found to be in the HLA-dependent T8+ lymphocyte subset. Considering that gamma IFN has an antiviral effect on persistent HAV infection in vitro and that it probably accounts for stimulation of HLA class I antigen expression on hepatocytes, our experimental results presented here demonstrate that human gamma IFN produced by HAV-specific T cells may participate in pathogenesis of hepatitis A infection in humans.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blackman M. J., Morris A. G. The effect of interferon treatment of targets on susceptibility to cytotoxic T-lymphocyte killing: augmentation of allogeneic killing and virus-specific killing relative to viral antigen expression. Immunology. 1985 Nov;56(3):451–457. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukowski J. F., Welsh R. M. Interferon enhances the susceptibility of virus-infected fibroblasts to cytotoxic T cells. J Exp Med. 1985 Jan 1;161(1):257–262. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.1.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins T., Korman A. J., Wake C. T., Boss J. M., Kappes D. J., Fiers W., Ault K. A., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Strominger J. L., Pober J. S. Immune interferon activates multiple class II major histocompatibility complex genes and the associated invariant chain gene in human endothelial cells and dermal fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4917–4921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Vos R., De Wolf-Peeters C., van den Oord J. J., Desmet V. A recommended procedure for ultrastructural immunohistochemistry on small human tissue samples. J Histochem Cytochem. 1985 Sep;33(9):959–964. doi: 10.1177/33.9.3860562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Vos R., De Wolf-Peeters C., van den Oord J. J., Desmet V. Ultrastructural immunocytochemical demonstration of HLA class I antigens in human pathological liver tissue. Hepatology. 1985 Nov-Dec;5(6):1071–1075. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840050602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dienstag J. L., Popper H., Purcell R. H. The pathology of viral hepatitis types A and B in chimpanzees. A comparison. Am J Pathol. 1976 Oct;85(1):131–148. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flehmig B. Hepatitis A virus in cell culture. II. Growth characteristics of hepatitis A virus in Frhk-4/R cells. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1981;170(2):73–81. doi: 10.1007/BF02122671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flehmig B., Vallbracht A., Wurster G. Hepatitis A virus in cell culture. III. Propagation of hepatitis A virus in human embryo kidney cells and human embryo fibroblast strains. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1981;170(2):83–89. doi: 10.1007/BF02122672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabriel P., Vallbracht A., Flehmig B. Lack of complement-dependent cytolytic antibodies in hepatitis A virus infection. J Med Virol. 1986 Sep;20(1):23–31. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890200105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauss-Müller V., Deinhardt F. Effect of hepatitis A virus infection on cell metabolism in vitro. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1984 Jan;175(1):10–15. doi: 10.3181/00379727-175-41757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein J. R., Raulet D. H., Pasternack M. S., Bevan M. J. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes produce immune interferon in response to antigen or mitogen. J Exp Med. 1982 Apr 1;155(4):1198–1203. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.4.1198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreth H. W., Kress L., Kress H. G., Ott H. F., Eckert G. Demonstration of primary cytotoxic T cells in venous blood and cerebrospinal fluid of children with mumps meningitis. J Immunol. 1982 Jun;128(6):2411–2415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreth H. W., ter Meulen V., Eckert G. Demonstration of HLA restricted killer cells in patients with acute measles. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1979 Jan 24;165(4):203–214. doi: 10.1007/BF02152920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurane I., Binn L. N., Bancroft W. H., Ennis F. A. Human lymphocyte responses to hepatitis A virus-infected cells: interferon production and lysis of infected cells. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):2140–2144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampson L. A., Fisher C. A. Weak HLA and beta 2-microglobulin expression of neuronal cell lines can be modulated by interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6476–6480. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Maza O., Andersson U., Andersson J., Britton S., De Ley M. Spontaneous production of interferon-gamma in adult and newborn humans. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):251–255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMichael A. J., Gotch F. M., Noble G. R., Beare P. A. Cytotoxic T-cell immunity to influenza. N Engl J Med. 1983 Jul 7;309(1):13–17. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198307073090103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris A. G., Lin Y. L., Askonas B. A. Immune interferon release when a cloned cytotoxic T-cell line meets its correct influenza-infected target cell. Nature. 1982 Jan 14;295(5845):150–152. doi: 10.1038/295150a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pignatelli M., Waters J., Brown D., Lever A., Iwarson S., Schaff Z., Gerety R., Thomas H. C. HLA class I antigens on the hepatocyte membrane during recovery from acute hepatitis B virus infection and during interferon therapy in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology. 1986 May-Jun;6(3):349–353. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840060303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirovino M., Aguet M., Huber M., Altorfer J., Schmid M. Absence of detectable serum interferon in acute and chronic viral hepatitis. Hepatology. 1986 Jul-Aug;6(4):645–647. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840060416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rakela J., Ishizawa L. Failure to detect circulating interferon during acute viral hepatitis. J Infect Dis. 1984 May;149(5):831–831. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.5.831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor P. E., Zuckerman A. J. Non-production of interfering substances by serum from patients with infectious hepatitis. J Med Microbiol. 1968 Nov;1(2):217–219. doi: 10.1099/00222615-1-2-217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinchieri G., Santoli D. Anti-viral activity induced by culturing lymphocytes with tumor-derived or virus-transformed cells. Enhancement of human natural killer cell activity by interferon and antagonistic inhibition of susceptibility of target cells to lysis. J Exp Med. 1978 May 1;147(5):1314–1333. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.5.1314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallbracht A., Gabriel P., Maier K., Hartmann F., Steinhardt H. J., Müller C., Wolf A., Manncke K. H., Flehmig B. Cell-mediated cytotoxicity in hepatitis A virus infection. Hepatology. 1986 Nov-Dec;6(6):1308–1314. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840060614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallbracht A., Gabriel P., Zahn J., Flehmig B. Hepatitis A virus infection and the interferon system. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jul;152(1):211–213. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.1.211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallbracht A., Hofmann L., Wurster K. G., Flehmig B. Persistent infection of human fibroblasts by hepatitis A virus. J Gen Virol. 1984 Mar;65(Pt 3):609–615. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-3-609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallbracht A., Treuner J., Manncke K. H., Niethammer D. Autoantibodies against human beta interferon following treatment with interferon. J Interferon Res. 1982;2(1):107–110. doi: 10.1089/jir.1982.2.107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virelizier J. L., Chan E. L., Allison A. C. Immunosuppressive effects of lymphocyte (type II) and leucocyte (type I) interferon on primary antibody responses in vivo and in vitro. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Nov;30(2):299–304. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada Y. K., Meager A., Yamada A., Ennis F. A. Human interferon alpha and gamma production by lymphocytes during the generation of influenza virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Gen Virol. 1986 Nov;67(Pt 11):2325–2334. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-11-2325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshie O., Schmidt H., Reddy E. S., Weissman S., Lengyel P. Mouse interferons enhance the accumulation of a human HLA RNA and protein in transfected mouse and hamster cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13169–13172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Doherty P. C. H-2 compatability requirement for T-cell-mediated lysis of target cells infected with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. Different cytotoxic T-cell specificities are associated with structures coded for in H-2K or H-2D;. J Exp Med. 1975 Jun 1;141(6):1427–1436. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.6.1427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



