Figure 5.
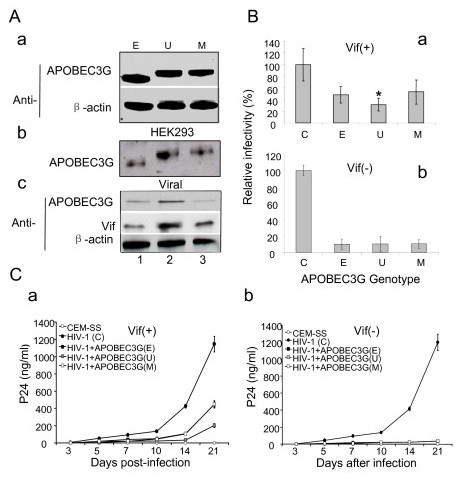
APOBEC3G fused with UBA2 confers stronger suppressive effect on viral infectivity than APOBEC3G. A. Packaging of different APOBEC3G variants into HIV-1 viral particles from HEK293 cells that stably express high level of APOBEC3G, APOBEC3G-UBA2 or APOBEC3G-UBA2*. a, The HEK293 cells that stably producing high level of APOBEC3G, APOBEC3G-UBA2 or APOBEC3G-UBA2* were established by selection of hygromycin resistant cells (300 μg/ml) for 2 weeks and verified by the Western blot analyses; b, Different APOBEC3G variants were equally packaged into the HIV-1 viral particles and harvested from HEK293 cells by expressing pNL4-3 plasmid in the control HEK293 cells lack of APOBEC3G (C) or HEK293 cells stably expressing different APOBEC3G variants; c, effect of viral expressing Vif on protein degradation of APOBEC3G variants. B. Effect of APOBEC3G variants on viral infectivity in MAGI-CCR5 cells. The MAGI-CCR5 cells were infected with viral supernatants harvested from the HEK293 cells that stably produce either no APOBEC3G or high level of different APOBEC3G constructs. Forty-eight hours post-infection, cells were stained by β-galactosidase for HIV-infected cells as described previously [43]. The viral infectivity of APOBEC3G-negative control HEK293 cells (C) was calibrated to 100% for comparison purpose. The viral infectivity was determined by comparing the total number of blue cells with the total number of cells counted. Data shown represent average of three independent experiments. Error Bars shown are standard errors of the means. a. results of wild type Vif(+) HIV-1NL4-3 infection; b. results of Vif(-) HIV-1NL4-3ΔVif infection. * p < 0.01. C. Effect of APOBEC3G variants on spread viral infection in CEM-SS cells. CEM-SS cells expressing APOBEC3G(E), APOBEC3G-UBA2(U), or APOBEC3G-UBA2(M) was infected by Vif(+) or Vif(-) HIV-1NL4-3. P24 antigen was measured post-infected day 3, 5, 7, 10 14, 21. a. results of wild type Vif(+) HIV-1NL4-3 infection; b. results of Vif(-) HIV-1NL4-3 Δ Vif infection.
