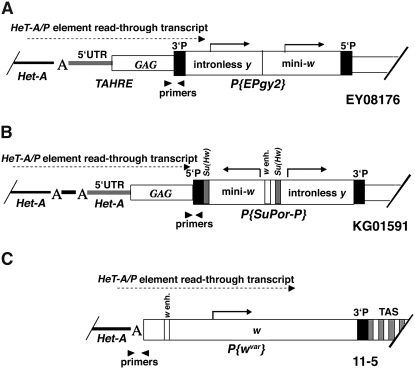
Figure 5.—
Diagram showing the structure of P-element insertions used in the experiment to measure HeT-A/P-element readthrough transcript levels. (A) EY08176 has a single EPgy2 element, containing an intronless yellow (y) gene and a mini-white (mini-w) gene. The EPgy2 construct is inserted in inverted orientation into the GAG open reading frame (ORF) of a TAHRE element >8 kb from the 2R chromosome end and >15 kb from TAS. The TAHRE bearing the insertion is bordered by an upstream HeT-A element. (B) KG01591 carries a SuPor-P element with a mini-w gene containing the w enhancer and an intronless y gene inserted 5 kb from 3R TAS. The mini-w is bordered by Su(Hw) insulators. The SuPor-P is inserted into the ORF of a HeT-A element. Directly upstream of this HeT-A lies a 168-bp HeT-A fragment with an oligo (A) tail followed by a 3′ HeT-A UTR with another oligo (A) tail. (C) 11-5 contains P{wvar} carrying a w transgene inserted between the HTT array and a truncated 2L TAS region. The P-element construct lacks its 5′ end (Biessmann et al. 2005a; Capkova Frydrychova et al. 2007). Arrowheads indicate the positions of primers used to quantify HeT-A/P-element readthrough transcript. “A” indicates the HeT-A oligo(A) tail. The presence of the HeT-A/P-element readthrough transcripts in all three insertions was reported previously (Capkova Frydrychova et al. 2007).