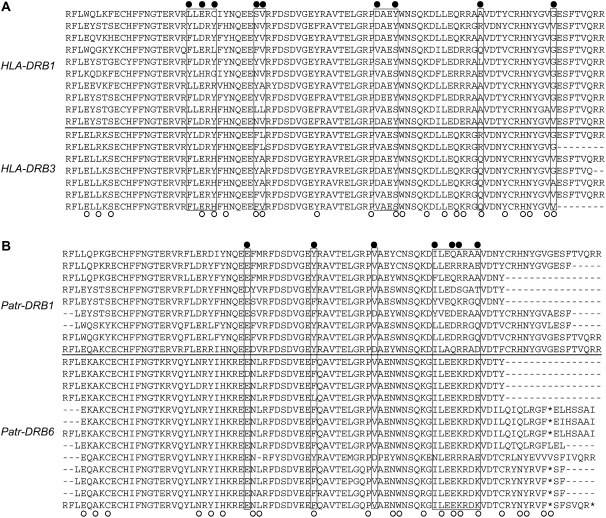
Figure 2.—
Amino acid sequence alignments of alleles in duplicated DRB genes in humans and chimpanzees. Data are from the IMGT/HLA and IMGT/MHC databases (Robinson et al. 2003). The open circles indicate amino acids involved in peptide-binding regions (PBRs) in humans (Brown et al. 1993). The solid circles represent shared polymorphic sites, which is a strong signature of gene conversion (Innan 2003). Putative gene conversion tracts are boxed. (A) DRB1 vs. DRB3 in humans. (B) DRB1 vs. DRB6 (pseudogene) in chimpanzees.