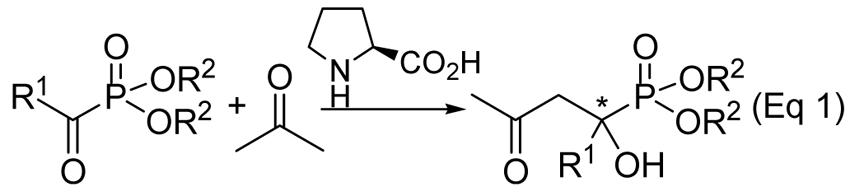
Table 1.
Enantioselective Synthesis of α-Hydroxy Phosphonatesa
 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| entry | R1 | R2 | T (°C) |
time (h) |
yield (%)b |
ee (%)c |
| 1 | Ph | Et | rt | 24 | 85 | 71 |
| 2 | Ph | Et | −30 | 96 | 65 | 87 |
| 3 | Ph | Me | −30 | 96 | 66 | 95 |
| 4 | Ph | i-Pr | −30 | 120 | 60 | 96 |
| 5 | p-Cl-C6H4 | Et | −30 | 96 | 68 | 91 |
| 6 | p-Cl-C6H4 | i-Pr | −30 | 96 | 63 | 95 |
| 7 | p-F-C6H4 | Et | −30 | 120 | 47 | 80 |
| 8 | p-F-C6H4 | i-Pr | −30 | 120 | 68d | 96 |
| 9 | p-Br-C6H4 | Et | −30 | 96 | 66 | >99 |
| 10 | p-I-C6H4 | Et | −30 | 96 | 67 | 94 |
| 11 | p-Me-C6H4 | Et | −30 | 96 | 63d | 85 |
| 12 | p-MeO-C6H4 | Et | −30 | 96 | 32d | 86 |
| 13 | Me | Et | rt | 24 | 94 | 92 |
| 14 | Me | Et | 0 | 72 | 91 | 97 |
| 15 | PhCH2 | Et | rt | 24 | 86d | 92 |
| 16 | PhCH2CH2 | Et | rt | 48 | 76 | 81 |
| 17 | trans-CH3CH=CH | Et | −30 | 108 | 67 | 98 |
All reactions were carried out with the ketophosphonate (0.50 mmol) in dry acetone (2.0 mL), with L-proline (0.10 mmol, 20 mol %) as the catalyst for the specified reaction time and temperature, unless otherwise specified.
Yield of isolated product after column chromatography.
Enantioselectivity was determined by HPLC analyses, the absolute configuration of the major enantiomer not determined.
With L-proline (0.25 mmol, 50 mol %) as the catalyst.
