Figure 6. Effect of 2-photon photolysis of Nv-VNA on nodose ganglion neurons.
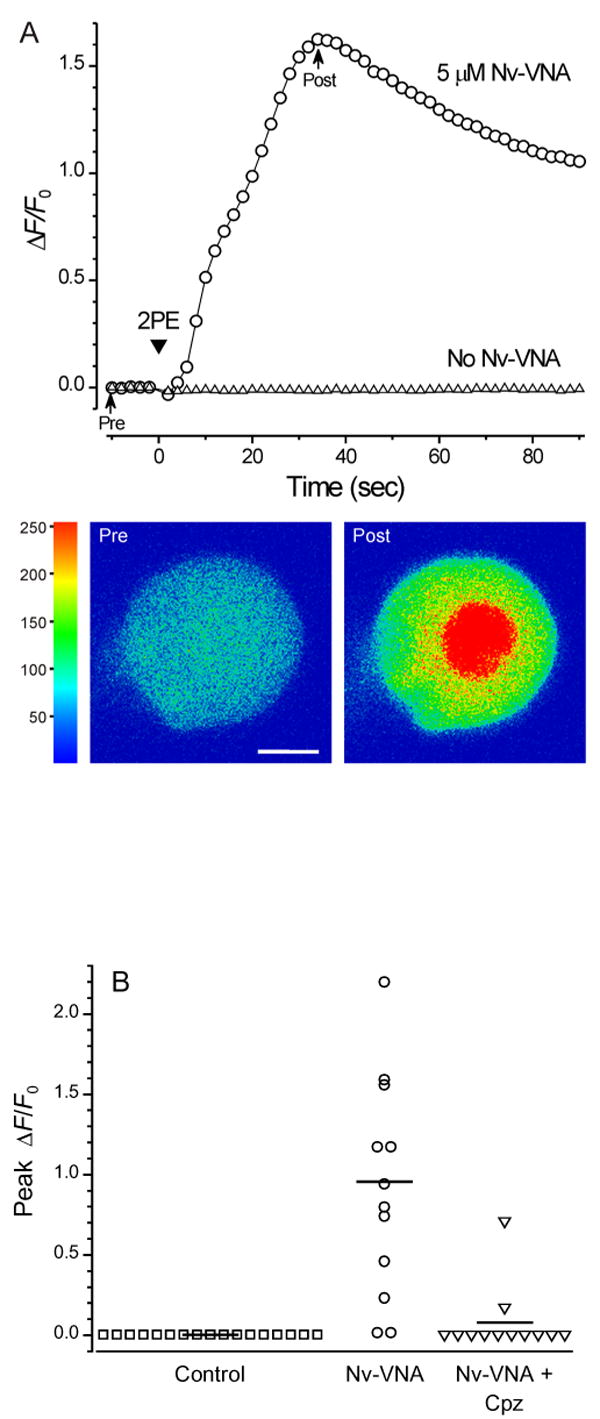
(A) In situ 2-photon photolysis of Nv-VNA evokes robust [Ca2+]i rises in nodose ganglion neurons. Fluorescence traces acquired in two separate experiments from single nodose ganglion neurons that had been loaded with the fluorescent Ca2+ indicator, fluo-3. When the neuron was superfused for 5 min with Locke solution containing 5 μM Nv-VNA, scanning 2-photon excitation (arrowhead marked “2PE”) evoked a sharp rise in [Ca2+]i (circles), as reflected by a large increase in fluo-3 fluorescence. In contrast, in a neuron not incubated with Nv-VNA, 2-photon excitation evoked no response (triangles). During 2-photon excitation, the Ti:S laser beam was scanned across the cell 10 times; each pixel (0.22 × 0.22 μm) received 16 μs of total exposure, corresponding to total exposure of ∼100 nJ per pixel, or ∼2 μJ/μm2. Representative pre- and post-photolysis confocal fluorescence images of the responsive neuron, corresponding to points in the trace marked by arrows, are shown below the graph. Fluorescence intensity in the images is encoded in pseudocolor. Scale bar = 10 μm.
(B) The [Ca2+]i rise in nodose ganglion neurons evoked by 2-photon photolysis of Nv-VNA is blocked by capsazepine, a vanilloid receptor antagonist. None of 17 control neurons exposed to the pulsed 720-nm emission from a titanium-sapphire laser in the absence of Nv-VNA showed a [Ca2+]i response. In the presence of 5 μM Nv-VNA, the same exposure to 720-nm light evoked [Ca2+]i rises in 12 of 14 neurons. In the presence of 5 μM Nv-VNA and 5 μM capsazepine (Cpz, a vanilloid antagonist), the same exposure to 720-nm light triggered a significant response in only 1 out of 11 neurons. Solid horizontal lines indicate the mean peak ΔF/F0 for each population: control, 0.003 ± 0.0008 (n = 17); in presence of Nv-VNA, 0.96 ± 0.17 (n = 14); in presence of Nv-VNA and Cpz, 0.078 ± 0.0593 (n = 12).
