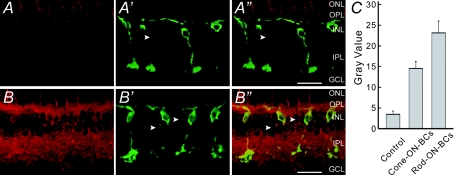
Figure 2. Confocal micrographs of the carp retinae showing an increased [cGMP]i by melatonin.
A, vertical section of the carp retina that was incubated with Ringer solution for 5 min and then labelled with the cGMP antibody. A′, micrograph of the same section labelled with the antibody against PKC. Note that several BCs that were strongly labelled by PKC could be Rod-ON-BCs, whereas one that was faintly labelled could be a Cone-ON-BC (arrowhead). A″, overlapped image of A and A′. B, vertical section of the carp retina that was incubated with 100 nm melatonin for 5 min and then labelled with the cGMP antibody. B′, micrograph of the same section labelled with the antibody against PKC. B″, overlapped image of B and B′, showing that the Rod-ON-BCs are intensively double-labelled, including the dendrites, somata and enlarged characteristic axon terminals. Several BCs, which were lightly labelled by PKC (arrowheads) and could be Cone-ON-BCs, were also cGMP-positive. All the micrograghs were obtained by single optical sectioning at intervals of 1.0 μm. ONL, outer nuclear layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; GCL, ganglion cell layer. Scale bars, 20 μm. C, bar chart, showing that melatonin induces an increase in [cGMP]i in both Rod- and Cone-ON-BCs. Grey values were determined in these two BC groups after incubation of 100 nm melatonin and compared to those obtained in normal Ringer solution. P = 0.0003 and 0.0004 (unpaired) for Rod-ON-BCs and Cone-ON-BCs, respectively. Error bars show ± s.e.m.