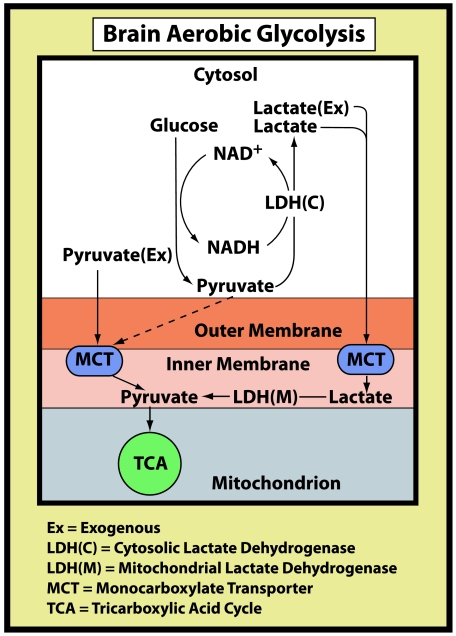
Figure 1. A schematic illustration of the brain glycolytic pathway under aerobic conditions.
A schematic illustration of the brain glycolytic pathway under aerobic conditions in which glucose is broken down to the glycolytic end-product lactate. Lactate, in turn, becomes the mitochondrial substrate, via its conversion to pyruvate, for the tricarboxylic acid cycle. At maximal work load, as measured in the study of Larsen et al. (2008) most of the lactate that is utilized by brain mitochondria is muscular in origin and thus exogenous. Under resting conditions, most of the lactate used by brain mitochondria originates from glucose that is metabolized glycolytically in neurons and glia.