Fig. 2.
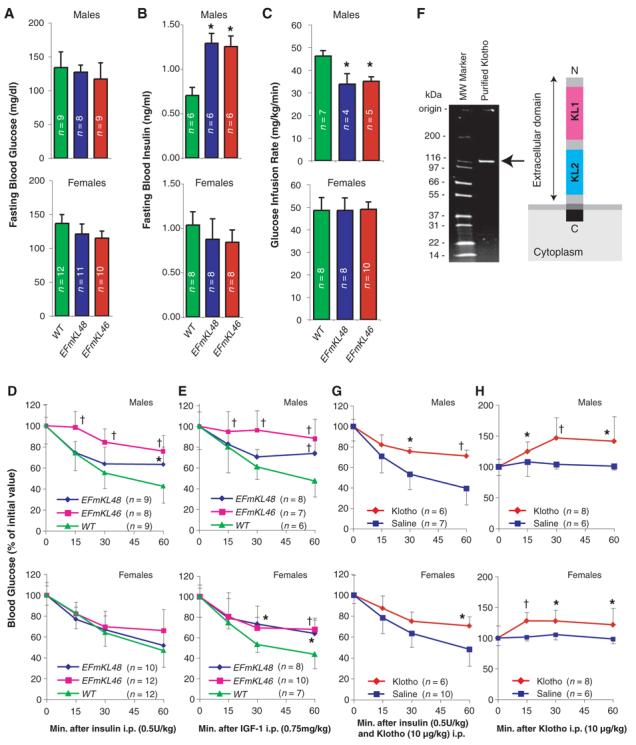
Klotho increases resistance to insulin and IGF1. (A and B) Fasting blood glucose (A) and insulin (B) levels were compared between wild-type (WT), EFmKL48, and EFmKL46 mice. (C) Hyperinsulinemic euglycemic clamp experiments. Glucose infusion rate (mg/kg/min) was compared between wild-type, EFmKL48, and EFmKL46 mice. During the clamp experiments there were no differences in blood glucose concentration between wild-type, EFmKL46, and EFmKL48 mice. The number of animals (n) for each group is indicated in the bars. (D and E) Insulin (D) and IGF1 (E) tolerance tests. Blood glucose levels after injection of insulin (0.5 U/kg) or IGF1 (0.75 mg/kg) were expressed as a percentage change from blood glucose concentration at time zero. Error bars indicate SD. *, P < 0.05 and †, P < 0.01 versus wild-type mice by ANOVA. (F) A schematic representation of Klotho extracellular peptide (right) and analysis of purified recombinant Klotho peptide by SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (left). (G) The effect of Klotho injection on insulin tolerance in mice. Insulin tolerance tests were performed with age-matched wild-type mice immediately after intraperitoneal injection with saline or purified recombinant Klotho peptide (10 μg/kg). (H) The effect of Klotho injection on blood glucose levels. Saline or Klotho protein (10 μg/kg) was administered into age-matched wild-type mice by intraperitoneal injection. Error bars indicate SD. *, P < 0.05 and †, P < 0.01 versus saline-injected mice by ANOVA.
