Figure 3.
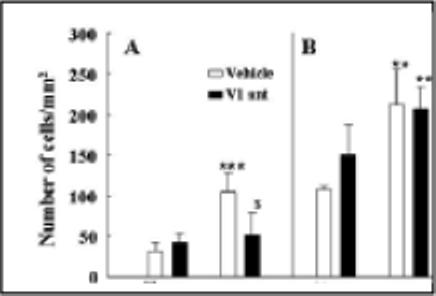
The effect of chronic osmotic minipump administration of the non-selective V1 receptor antagonist, dGly[Phaa1,D-tyr(et), Lys, Arg]VP (V1R Ant), or vehicle for 14 days on plasma ACTH responses to the novel stress of i.p. hypertonic saline injection (ipHS) in conscious naïve control rats (A), or rats subjected to restraint stress for 1h daily for 14 days (B). Data are the mean and SE of values obtained in 8 to 10 rats per group. Both groups showed a significant effect of ipHS on plasma ACTH levels (*, p<0.001). ACTH responses to ipHS in naïve rats were significantly reduced by the V1R Ant compared with the vehicle infused controls ($, p<0.04). ACTH responses to ipHS in repeatedly restrained rats were significantly higher than those in naïve rats (#, p<0.02), and these enhanced responses were unaffected by the V1R Ant.
