FIG. 2.
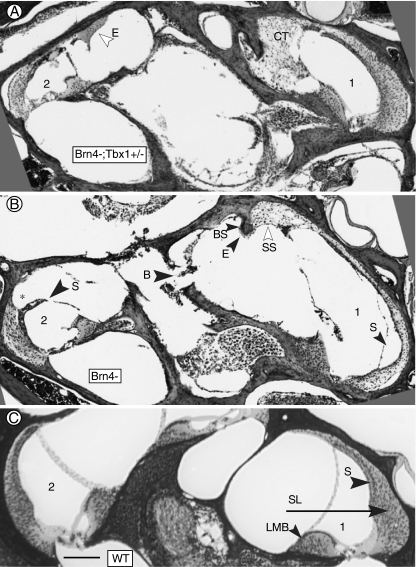
Defects in the basal turn of mutant mice. A Basal turn of a Brn4−;Tbx1+/− mouse. Excessive connective tissue (CT) has filled the space normally occupied by perilymph in the scala vestibuli. Abnormal eosinophilic material (E) is present in the upper basal turn. B Basal turn of a Brn4− mouse. Hypertrophied suprastrial connective tissue (SS) is present in the lower basal turn, and the stria vascularis (S) is missing. Note the adjacent spiral ligament is much thinner than in the corresponding area in A and C. In the upper basal turn, the spiral ligament is missing (asterisk) where it would normally be attached to the stria vascularis, and there are voids in the modiolar bone (B). C Basal turn of wild type cochlea showing normal morphology. (1) and (2) indicate lower basal and upper basal half-turns, respectively. B, missing bone; BS, bone spur; CT, connective tissue; E, eosinophillic substance; LMB, spiral limbus; SL, spiral ligament; S, stria vascularis; and SS, suprastrial region. The bar inC indicates 100 μm.