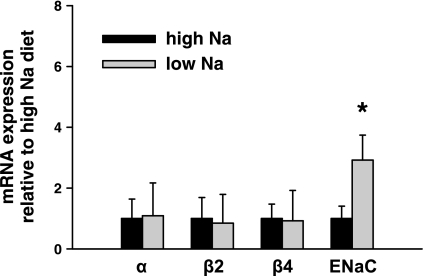
Fig. 1.
Effect of dietary Na+ intake on large-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ (BK) channel and epithelial Na+ channel (ENaC) subunit transcript expression in single cortical collecting ducts (CCDs). Real-time PCR was used to examine the expression of α-, β1-, β2-, and β4-subunits and α-ENaC mRNA in single CCDs isolated from rabbits fed a high (HS)-or low (LS)-Na+ diet. Channel subunit-specific mRNA abundance in CCDs harvested from LS-fed animals, normalized to that of 18S measured in the same sample, is presented as the fold difference relative to the ratio detected in tubules isolated from HS-fed rabbits. BK α (n = 10), β2 (n = 8), and β4 (n = 10) mRNA expression in CCDs isolated from HS-fed animals did not significantly differ from that detected in LS-fed animals (n = 12, 11, 13, respectively; P = nonsignificant). β1-Subunit transcripts were not detected in any CCD sample. α-ENaC mRNA expression in CCDs isolated from LS-fed animals (n = 6) significantly exceeded that detected in HS-fed animals (n = 10). Values are means ± SE. *P < 0.05 compared with HS.