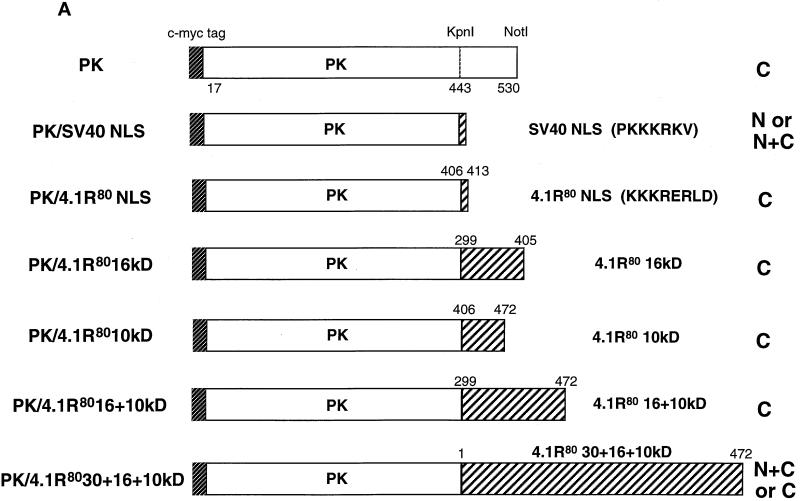
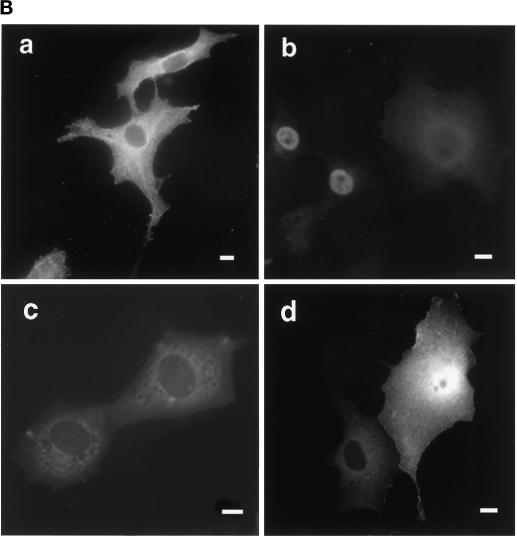
Figure 4.
Constructs used to identify protein 4.1R domains necessary for targeting cytoplasmic PK to the nucleus. (A) The top construct corresponds to PK lacking its first 16 amino acids, which are replaced by a c-myc epitope tag (Siomi and Dreyfuss, 1995). A construct consisting of PK fused with a KpnI–NotI fragment encoding SV40 NLS (PKKKRKV; Kalderon et al., 1984) was used as a positive control. The PK clone was used to generate fusion proteins with KpnI–NotI fragments encoding various 4.1R domains. Numbers displayed above dashed boxes refer to the 4.1R80 amino acids present in each KpnI–NotI fragment. The predominant distribution pattern is displayed for each construct and is based on examination of at least 600 cells per construct. N, strong nuclear staining with no or weak cytoplasmic staining; C, strong cytoplasmic staining with no nuclear staining; N+C, variable nuclear staining and strong cytoplasmic staining. (B) COS-7 cells transfected with the various c-myc epitope-tagged PK fusion proteins were fixed with 3% paraformaldehyde, permeabilized with 0.5% Triton X-100, and processed for immunofluorescence using a monoclonal anti-c-myc epitope tag antibody as primary antibody and anti-mouse IgG coupled to Texas Red as secondary antibody. Cells were transfected with the following: (a) PK; (b) PK/SV40 NLS; (c) PK/4.1R80KKKRERLD (including amino acids 406–413); (d) PK/4.1R8030 + 16 + 10 kDa (including amino acids 1–472). The image b shows a representative population of the two major patterns observed: strong nuclear and weak cytoplasmic staining or similar nuclear and cytoplasmic staining accounting for 45 and 30% of transfected cells, respectively, 25% of the cells showing no nuclear staining. The image in d shows a representative population of the two major patterns observed: nuclear and cytoplasmic staining or only cytoplasmic staining accounting for 45 and 55% of transfected cells, respectively. An identical pattern was observed if sequences of the 10-kDa domain encoded by exon 17 were deleted (our unpublished results). Nuclear localization was not observed for several fusion constructs containing either the 16-kDa domain (PK/4.1R8016 kDa, including amino acids 299–406) or the NLS with additional flanking sequences (PK/4.1R8010 kDa, including amino acids 406–472; PK/4.1R8016 + 10 kDa, including amino acids 299–472). Bar, 10 μm.