Abstract
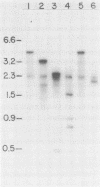
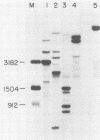
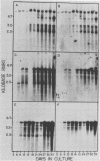
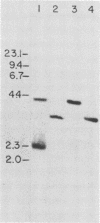
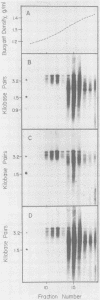
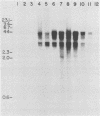
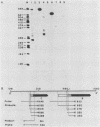
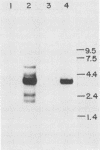
Clonal cells derived from HepG2 cells transfected with a plasmid containing hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA secrete hepatitis B surface antigen particles, nucleocapsids, and virions (M. A. Sells, M.-L. Chen, and G. Acs, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84:1005-1009, 1987) which elicit acute hepatitis in chimpanzees (G. Acs, M. A. Sells, R. H. Purcell, P. Price, R. Engle, M. Shapiro, and H. Popper, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84:4641-4644, 1987). We report here the initial characterization of the viral nucleic acids produced in this culture system. Kinetic analyses of nuclear, cytoplasmic, and extracellular HBV DNAs were performed by Southern blotting with radiolabeled HBV strand-specific probes. The results from these analyses indicate that at the stationary cellular growth phase, there is a dramatic increase in the rate at which HBV DNA accumulates. Incomplete double- and single-stranded forms of the HBV genome were detected in the nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions as well as in the extracellular medium. In addition, the nuclear DNA apparently includes multiple complete copies of the HBV genome chromosomally integrated and full-length covalently closed circular HBV DNA. Multiple HBV-specific polyadenylated RNAs with lengths of 3.5, 2.5, and 2.1 kilobases were identified by Northern (RNA) blot analysis. S1 nuclease mapping and primer extension identified a single 3' end and multiple unique initiation sites corresponding to nucleotides just 5' to the pre-S1 region, as well as upstream and within the pre-S2 and precore regions. The nucleic acid profile obtained from these analyses is essentially a facsimile of that obtained by studying liver tissue from HBV-infected individuals.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acs G., Sells M. A., Purcell R. H., Price P., Engle R., Shapiro M., Popper H. Hepatitis B virus produced by transfected Hep G2 cells causes hepatitis in chimpanzees. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4641–4644. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
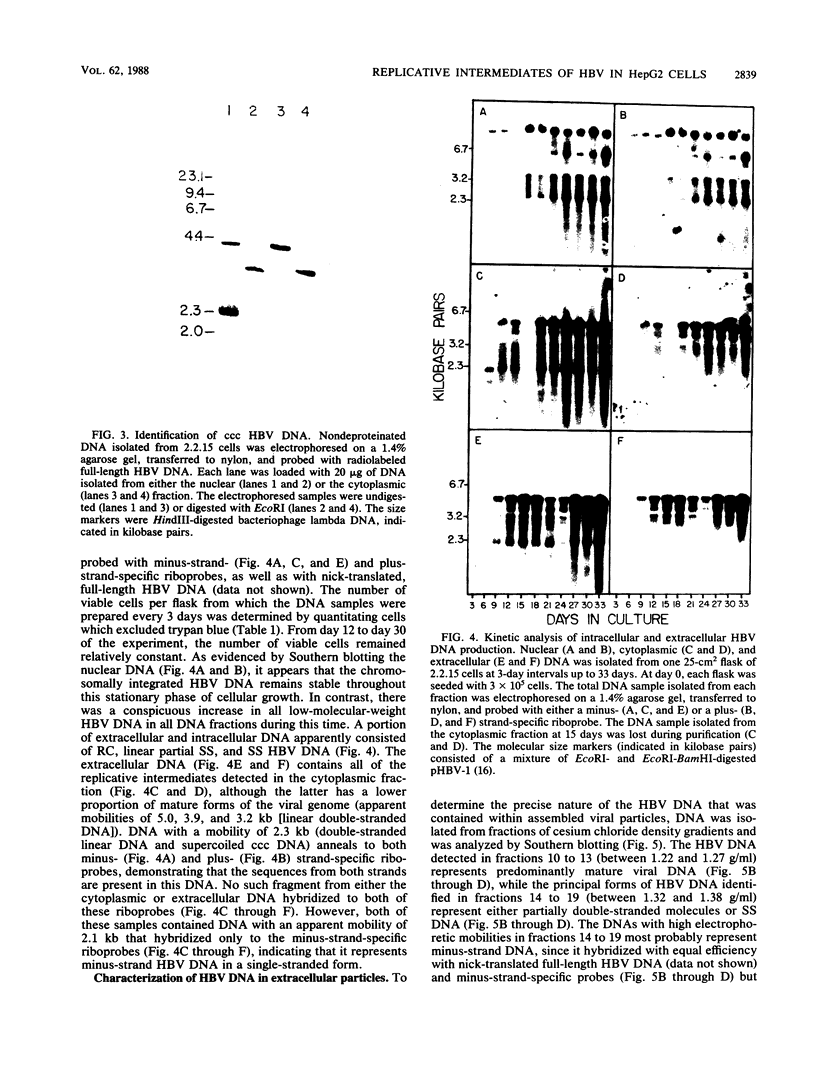
- Blum H. E., Haase A. T., Harris J. D., Walker D., Vyas G. N. Asymmetric replication of hepatitis B virus DNA in human liver: demonstration of cytoplasmic minus-strand DNA by blot analyses and in situ hybridization. Virology. 1984 Nov;139(1):87–96. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90332-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broome S., Gilbert W. Rous sarcoma virus encodes a transcriptional activator. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):537–546. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90202-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büscher M., Reiser W., Will H., Schaller H. Transcripts and the putative RNA pregenome of duck hepatitis B virus: implications for reverse transcription. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):717–724. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90220-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattaneo R., Will H., Hernandez N., Schaller H. Signals regulating hepatitis B surface antigen transcription. Nature. 1983 Sep 22;305(5932):336–338. doi: 10.1038/305336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattaneo R., Will H., Schaller H. Hepatitis B virus transcription in the infected liver. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):2191–2196. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02113.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. M., Jeng K. S., Hu C. P., Lo S. J., Su T. S., Ting L. P., Chou C. K., Han S. H., Pfaff E., Salfeld J. Production of hepatitis B virus in vitro by transient expression of cloned HBV DNA in a hepatoma cell line. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):675–680. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04807.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christman J. K., Gerber M., Price P. M., Flordellis C., Edelman J., Acs G. Amplification of expression of hepatitis B surface antigen in 3T3 cells cotransfected with a dominant-acting gene and cloned viral DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1815–1819. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enders G. H., Ganem D., Varmus H. E. 5'-terminal sequences influence the segregation of ground squirrel hepatitis virus RNAs into polyribosomes and viral core particles. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):35–41. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.35-41.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enders G. H., Ganem D., Varmus H. Mapping the major transcripts of ground squirrel hepatitis virus: the presumptive template for reverse transcriptase is terminally redundant. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):297–308. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80125-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
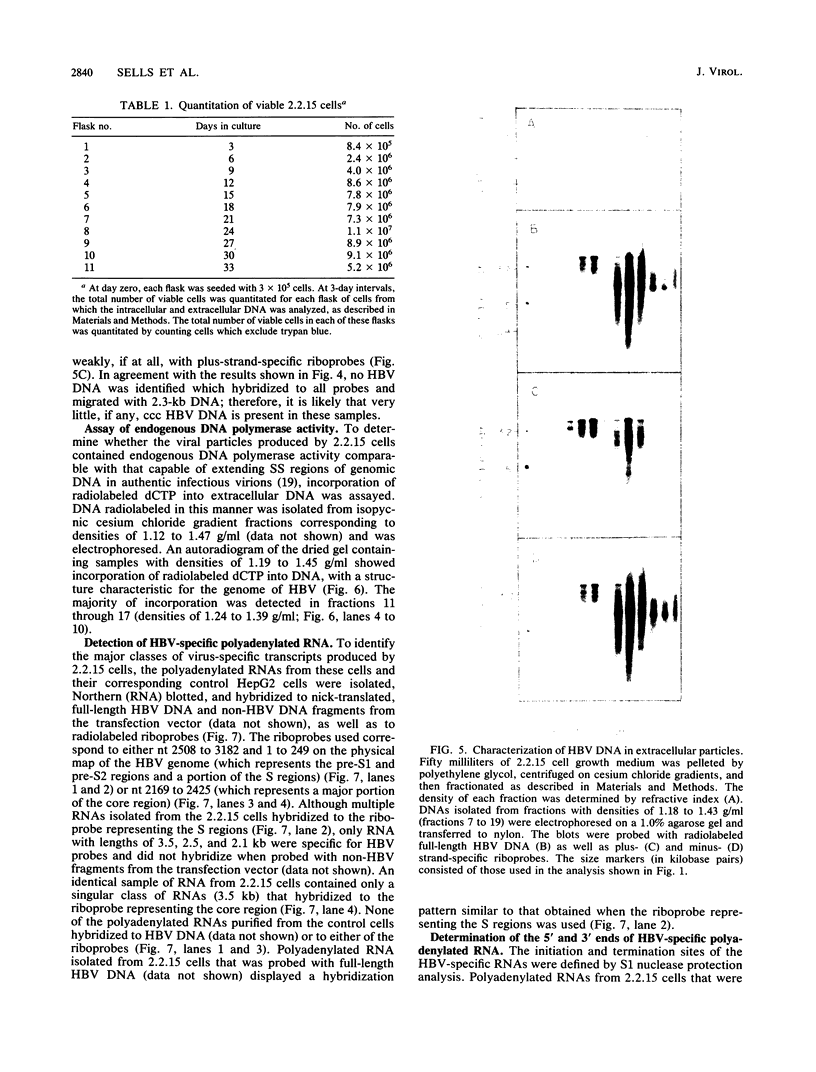
- Feitelson M. A., Millman I., Halbherr T., Simmons H., Blumberg B. S. A newly identified hepatitis B type virus in tree squirrels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2233–2237. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerlich W. H., Robinson W. S. Hepatitis B virus contains protein attached to the 5' terminus of its complete DNA strand. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):801–809. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90443-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschman S. Z., Price P., Garfinkel E., Christman J., Acs G. Expression of cloned hepatitis B virus DNA in human cell cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5507–5511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Flavell R. A. A physical map of the DNA regions flanking the rabbit beta-globin gene. Cell. 1977 Oct;12(2):429–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90119-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan P. M., Greenman R. L., Gerin J. L., Purcell R. H., Robinson W. S. DNA polymerase associated with human hepatitis B antigen. J Virol. 1973 Nov;12(5):995–1005. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.5.995-1005.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lien J. M., Aldrich C. E., Mason W. S. Evidence that a capped oligoribonucleotide is the primer for duck hepatitis B virus plus-strand DNA synthesis. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):229–236. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.229-236.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason W. S., Aldrich C., Summers J., Taylor J. M. Asymmetric replication of duck hepatitis B virus DNA in liver cells: Free minus-strand DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):3997–4001. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.3997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason W. S., Halpern M. S., England J. M., Seal G., Egan J., Coates L., Aldrich C., Summers J. Experimental transmission of duck hepatitis B virus. Virology. 1983 Dec;131(2):375–384. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90505-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. H., Marion P. L., Robinson W. S. Hepatitis B viral DNA-RNA hybrid molecules in particles from infected liver are converted to viral DNA molecules during an endogenous DNA polymerase reaction. Virology. 1984 Nov;139(1):64–72. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90330-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. H., Robinson W. S. Hepatitis B virus DNA forms in nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions of infected human liver. Virology. 1984 Sep;137(2):390–399. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90231-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möröy T., Etiemble J., Trépo C., Tiollais P., Buendia M. A. Transcription of woodchuck hepatitis virus in the chronically infected liver. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1507–1514. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03810.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurath A. R., Kent S. B., Strick N., Taylor P., Stevens C. E. Hepatitis B virus contains pre-S gene-encoded domains. Nature. 1985 May 9;315(6015):154–156. doi: 10.1038/315154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connell A. P., Urban M. K., London W. T. Naturally occurring infection of Pekin duck embryos by duck hepatitis B virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1703–1706. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall L. B., Standring D. N., Laub O., Rutter W. J. Transcription of hepatitis B virus by RNA polymerase II. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Oct;3(10):1766–1773. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.10.1766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. C., Mann D. A. Rapid transfer of DNA from agarose gels to nylon membranes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7207–7221. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeger C., Ganem D., Varmus H. E. Biochemical and genetic evidence for the hepatitis B virus replication strategy. Science. 1986 Apr 25;232(4749):477–484. doi: 10.1126/science.3961490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sells M. A., Chen M. L., Acs G. Production of hepatitis B virus particles in Hep G2 cells transfected with cloned hepatitis B virus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):1005–1009. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.1005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui A., Jameel S., Mapoles J. Transcriptional control elements of hepatitis B surface antigen gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):566–570. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standring D. N., Rutter W. J., Varmus H. E., Ganem D. Transcription of the hepatitis B surface antigen gene in cultured murine cells initiates within the presurface region. J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):563–571. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.563-571.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stibbe W., Gerlich W. H. Structural relationships between minor and major proteins of hepatitis B surface antigen. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):626–628. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.626-628.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers J., Mason W. S. Replication of the genome of a hepatitis B--like virus by reverse transcription of an RNA intermediate. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):403–415. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90157-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers J. Three recently described animal virus models for human hepatitis B virus. Hepatology. 1981 Mar-Apr;1(2):179–183. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840010215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sureau C., Romet-Lemonne J. L., Mullins J. I., Essex M. Production of hepatitis B virus by a differentiated human hepatoma cell line after transfection with cloned circular HBV DNA. Cell. 1986 Oct 10;47(1):37–47. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90364-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagawa M., Omata M., Yokosuka O., Uchiumi K., Imazeki F., Okuda K. Early events in duck hepatitis B virus infection. Sequential appearance of viral deoxyribonucleic acid in the liver, pancreas, kidney, and spleen. Gastroenterology. 1985 Dec;89(6):1224–1229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurimoto T., Fujiyama A., Matsubara K. Stable expression and replication of hepatitis B virus genome in an integrated state in a human hepatoma cell line transfected with the cloned viral DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(2):444–448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.2.444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuttleman J. S., Pourcel C., Summers J. Formation of the pool of covalently closed circular viral DNA in hepadnavirus-infected cells. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):451–460. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90602-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuttleman J. S., Pugh J. C., Summers J. W. In vitro experimental infection of primary duck hepatocyte cultures with duck hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 1986 Apr;58(1):17–25. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.1.17-25.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiser B., Ganem D., Seeger C., Varmus H. E. Closed circular viral DNA and asymmetrical heterogeneous forms in livers from animals infected with ground squirrel hepatitis virus. J Virol. 1983 Oct;48(1):1–9. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.1.1-9.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Will H., Reiser W., Weimer T., Pfaff E., Büscher M., Sprengel R., Cattaneo R., Schaller H. Replication strategy of human hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):904–911. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.904-911.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaginuma K., Shirakata Y., Kobayashi M., Koike K. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) particles are produced in a cell culture system by transient expression of transfected HBV DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2678–2682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]