Figure 7.
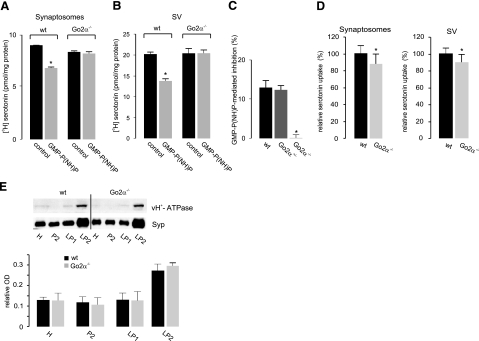
Go2α modulates [3H] monoamine uptake into VMAT2-containing SVs. A, B) SLO-permeabilized synaptosomes (A) or isolated SVs (B) of either wt or Go2α−/− mice were subjected to [3H] serotonin uptake in the absence or presence of 5 or 100 μM of GMP-P(NH)P, respectively. GMP-P(NH)P failed to modulate vesicular uptake in knockout animals. C) SVs from either wt, heterozygous, or knockout animals were subjected to serotonin uptake in the absence or presence of 100 μM GMP-P(NH)P. Values are expressed as the GMP-P(NH)P-mediated inhibition (%). Note that there is no inhibition in the knockout-derived SVs. D) [3H]serotonin uptake into permeabilized synaptosomes or isolated SVs is moderately decreased in Go2α−/− animals compared to wt littermates. Values were taken from 10 different experiments, each run in triplicate. The reserpine-sensitive uptake of wt animals was set at 100%. Bars indicate means ± sd. E) The amount of the vacuolar ATPase in various subcellular fractions analyzed using an antibody against the 116-kDa subunit revealed an enrichment in the SV fraction (LP2), with no difference between wt- and Go2α−/−-derived membranes. Graphs show the quantification from 10-μg protein load. Data were normalized to Syp; means ± sd; n = 4 animals/genotype. *P < 0.05.